GitHub is being abused to distribute the Lumma Stealer information-stealing malware as faux fixes posted in challenge feedback.
The marketing campaign was first reported by a contributor to the teloxide rust library, who famous on Reddit that they obtained 5 totally different feedback of their GitHub points that pretended to be fixes however had been as an alternative pushing malware.
Additional evaluation by BleepingComputer discovered hundreds of comparable feedback posted to a variety of tasks on GitHub, all providing faux fixes to different individuals’s questions.
The answer tells individuals to obtain a password-protected archive from mediafire.com or by means of a bit.ly URL and run the executable inside it. Within the present marketing campaign, the password has been “changeme” in all of the feedback we now have seen.
Reverse engineer Nicholas Sherlock instructed BleepingComputer that over 29,000 feedback pushing this malware had been posted over a 3-day interval.
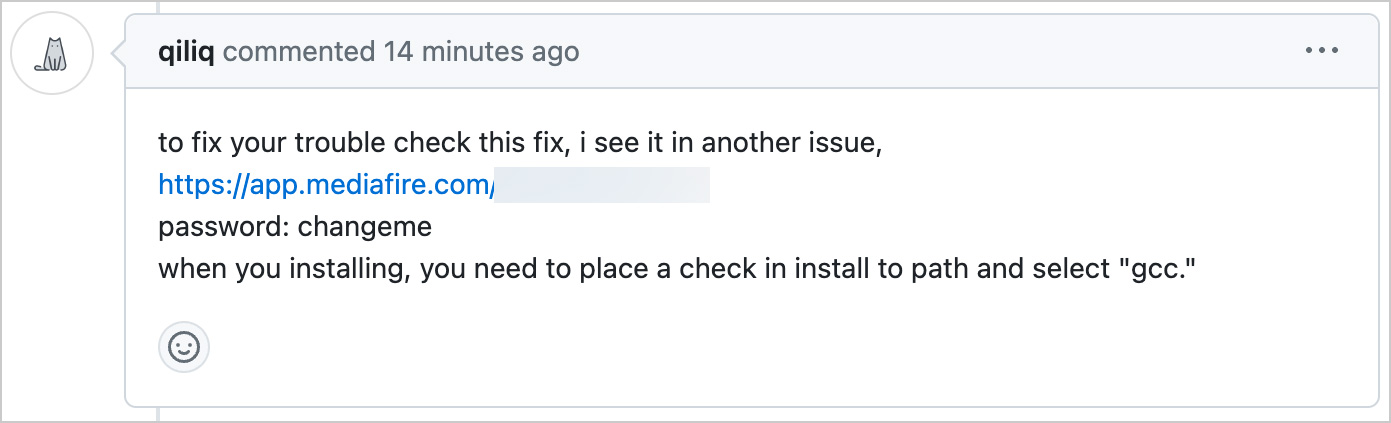
Supply: Andrey Brusnik
Clicking on the hyperlink brings guests to a obtain web page for a file referred to as ‘repair.zip,’ which incorporates a number of DLL recordsdata and an executable named x86_64-w64-ranlib.exe.
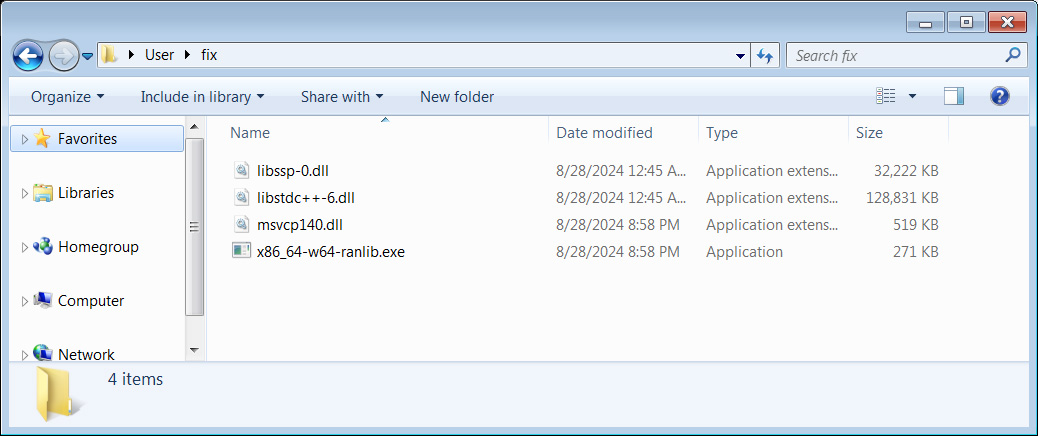
Supply: BleepingComputer
Operating the executable on Any.Run signifies it’s the Lumma Stealer information-stealing malware.
Lumma Stealer is a sophisticated data stealer that, when executed, makes an attempt to steal cookies, credentials, passwords, bank cards, and shopping historical past from Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox, and different Chromium browsers.
The malware can even steal cryptocurrency wallets, personal keys, and textual content recordsdata with names like seed.txt, move.txt, ledger.txt, trezor.txt, metamask.txt, bitcoin.txt, phrases, pockets.txt, *.txt, and *.pdf, as these are prone to comprise personal crypto keys and passwords.
This information is collected into an archive and despatched again to the attacker, the place they’ll use the data in additional assaults or promote it on cybercrime marketplaces.
Whereas GitHub Employees has been deleting these feedback as they’re detected, individuals have already reported falling for the assault.
For many who ran the malware, you should change the passwords at all of your accounts utilizing a novel password for every web site and migrate cryptocurrency to a brand new pockets.
Final month, Verify Level Analysis disclosed the same marketing campaign by the Stargazer Goblin menace actors, who created a malware Distribution-as-a-Service (DaaS) from over 3,000 faux accounts on GitHub to push information-stealing malware.
It’s unclear if this is identical marketing campaign or a brand new one carried out by totally different menace actors.
