What’s the web of issues (IoT)?
The web of issues, or IoT, is a community of interrelated gadgets that join and trade information with different IoT gadgets and the cloud. IoT gadgets are usually embedded with know-how equivalent to sensors and software program and might embrace mechanical and digital machines and shopper objects.
More and more, organizations in a wide range of industries are utilizing IoT to function extra effectively, ship enhanced customer support, enhance decision-making and enhance the worth of the enterprise.
With IoT, information is transferable over a community with out requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interactions.
A factor within the web of issues generally is a particular person with a coronary heart monitor implant, a farm animal with a biochip transponder, an vehicle that has built-in sensors to alert the motive force when tire strain is low, or some other pure or man-made object that may be assigned an Web Protocol handle and is ready to switch information over a community.
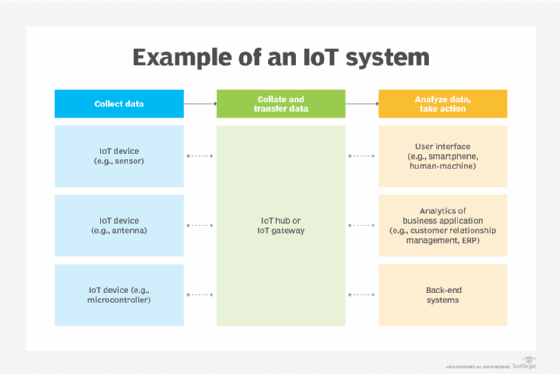
How does IoT work?
An IoT ecosystem consists of web-enabled sensible gadgets that use embedded techniques — equivalent to processors, sensors and communication {hardware} — to gather, ship and act on information they purchase from their environments.
IoT gadgets share the sensor information they accumulate by connecting to an IoT gateway, which acts as a central hub the place IoT gadgets can ship information. Earlier than the info is shared, it may also be despatched to an edge gadget the place that information is analyzed regionally. Analyzing information regionally reduces the amount of information despatched to the cloud, which minimizes bandwidth consumption.
Typically, these gadgets talk with different associated gadgets and act on the knowledge they get from each other. The gadgets do a lot of the work with out human intervention, though individuals can work together with the gadgets — for instance, to set them up, give them directions or entry the info.
The connectivity, networking and communication protocols used with these web-enabled gadgets largely depend upon the precise IoT functions deployed.
IoT also can use synthetic intelligence and machine studying to assist in making information assortment processes simpler and extra dynamic.
Why is IoT necessary?
IoT helps individuals dwell and work smarter. Customers, for instance, can use IoT-embedded gadgets — equivalent to automobiles, smartwatches or thermostats — to enhance their lives. For instance, when an individual arrives residence, their automobile might talk with the storage to open the door; their thermostat might modify to a preset temperature; and their lighting might be set to a decrease depth and coloration.
Along with providing sensible gadgets to automate properties, IoT is important to enterprise. It supplies organizations with a real-time look into how their techniques actually work, delivering insights into all the pieces from the efficiency of machines to provide chain and logistics operations.
IoT allows machines to finish tedious duties with out human intervention. Corporations can automate processes, scale back labor prices, reduce down on waste and enhance service supply. IoT helps make it inexpensive to fabricate and ship items, and gives transparency into buyer transactions.
IoT is without doubt one of the most necessary applied sciences and it continues to advance as extra companies notice the potential of related gadgets to maintain them aggressive.
What are the advantages of IoT to organizations?
IoT gives a number of advantages to organizations. Some advantages are industry-specific and a few are relevant throughout a number of industries. Frequent advantages for companies embrace the next:
- Screens total enterprise processes.
- Improves the client expertise.
- Saves money and time.
- Enhances worker productiveness.
- Offers integration and adaptable enterprise fashions.
- Permits higher enterprise choices.
- Generates extra income.
IoT encourages corporations to rethink how they method their companies and offers them the instruments to enhance their enterprise methods.
Typically, IoT is most plentiful in manufacturing, transportation and utility organizations that use sensors and different IoT gadgets; nevertheless, it additionally has use circumstances for organizations throughout the agriculture, infrastructure and residential automation industries, main some organizations towards digital transformation.
IoT can profit farmers in agriculture by making their job simpler. Sensors can accumulate information on rainfall, humidity, temperature and soil content material and IoT can assist automate farming strategies.
IoT also can assist monitor operations surrounding infrastructure. Sensors, for instance, can monitor occasions or modifications inside structural buildings, bridges and different infrastructure that would doubtlessly compromise security. This supplies advantages equivalent to improved incident administration and response, diminished prices of operations and improved high quality of service.
A house automation enterprise can use IoT to observe and manipulate mechanical and electrical techniques in a constructing. On a broader scale, sensible cities can assist residents scale back waste and power consumption.
IoT touches each {industry}, together with healthcare, finance, retail and manufacturing.
What are the professionals and cons of IoT?
Among the benefits of IoT embrace the next:
- Permits entry to data from anyplace at any time on any gadget.
- Improves communication between related digital gadgets.
- Permits the switch of information packets over a related community, which might save money and time.
- Collects giant quantities of information from a number of gadgets, aiding each customers and producers.
- Analyzes information on the edge, decreasing the quantity of information that must be despatched to the cloud.
- Automates duties to enhance the standard of a enterprise’s providers and reduces the necessity for human intervention.
- Permits healthcare sufferers to be cared for frequently and extra successfully.
Some disadvantages of IoT embrace the next:
- Will increase the assault floor because the variety of related gadgets grows. As extra data is shared between gadgets, the potential for a hacker to steal confidential data will increase.
- Makes gadget administration difficult because the variety of IoT gadgets will increase. Organizations may ultimately should take care of an enormous variety of IoT gadgets, and amassing and managing the info from all these gadgets might be difficult.
- Has the potential to deprave different related gadgets if there is a bug within the system.
- Will increase compatibility points between gadgets, as there is not any worldwide customary of compatibility for IoT. This makes it troublesome for gadgets from completely different producers to speak with one another.
IoT requirements and frameworks
Notable organizations which are concerned within the improvement of IoT requirements embrace the next:
- Worldwide Electrotechnical Fee.
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
- Industrial Web Consortium.
- Open Connectivity Basis.
- Thread Group.
- Connectivity Requirements Alliance.
Some examples of IoT requirements embrace the next:
- IPv6 over Low-Energy Wi-fi Private Space Networks (6LoWPAN) is an open customary outlined by the Web Engineering Process Pressure (IETF). This customary allows any low-power radio to speak to the web, together with 804.15.4, Bluetooth Low Power and Z-Wave for residence automation. Along with residence automation, this customary can also be utilized in industrial monitoring and agriculture.
- Zigbee is a low-power, low-data charge wi-fi community used primarily in residence and industrial settings. ZigBee relies on the IEEE 802.15.4 customary. The ZigBee Alliance created Dotdot, the common language for IoT that permits sensible objects to work securely on any community and perceive one another.
- Information Distribution Service (DDS) was developed by the Object Administration Group and is an industrial IoT (IIoT) customary for real-time, scalable and high-performance machine-to-machine (M2M) communication.
IoT requirements typically use particular protocols for gadget communication. A selected protocol dictates how IoT gadget information is transmitted and acquired. Some instance IoT protocols embrace the next:
- Constrained Software Protocol. CoAP is a protocol designed by the IETF that specifies how low-power, compute-constrained gadgets can function in IoT.
- Superior Message Queuing Protocol. The AMQP is an open supply revealed customary for asynchronous messaging by wire. AMQP allows encrypted and interoperable messaging between organizations and functions. The protocol is utilized in client-server messaging and in IoT gadget administration.
- Lengthy-Vary Vast Space Community (LoRaWAN). This protocol for WANs is designed to help enormous networks, equivalent to sensible cities, with tens of millions of low-power gadgets.
- MQ Telemetry Transport. MQTT is a light-weight protocol that is used for management and distant monitoring functions. It is appropriate for gadgets with restricted assets.
IoT frameworks embrace the next:
- Amazon Internet Providers (AWS) IoT is a cloud computing platform for IoT launched by Amazon. This framework is designed to allow sensible gadgets to simply join and securely work together with the AWS cloud and different related gadgets.
- Arm Mbed IoT is an open supply platform to develop apps for IoT primarily based on Arm microcontrollers. The objective of this IoT platform is to supply a scalable, related and safe setting for IoT gadgets by integrating Mbed instruments and providers.
- Microsoft Azure IoT Suite platform is a set of providers that permit customers work together with and obtain information from their IoT gadgets, in addition to carry out varied operations over information, equivalent to multidimensional evaluation, transformation and aggregation, and visualize these operations in a approach that is appropriate for enterprise.
- Calvin is an open supply IoT platform from Ericsson designed for constructing and managing distributed functions that permit gadgets discuss to one another. Calvin features a improvement framework for software builders, in addition to a runtime setting for dealing with the operating software.
Client and enterprise IoT functions
There are quite a few real-world functions of the web of issues, starting from shopper IoT and enterprise IoT to manufacturing and IIoT. IoT functions span quite a few verticals, together with automotive, telecom and power.
Within the shopper section, for instance, sensible properties which are outfitted with sensible thermostats, sensible home equipment and related heating, lighting and digital gadgets may be managed remotely by way of computer systems and smartphones.
Wearable gadgets with sensors and software program can accumulate and analyze consumer information, sending messages to different applied sciences in regards to the customers with the purpose of creating customers’ lives simpler and extra comfy. Wearable gadgets are additionally used for public security — for instance, by bettering first responders’ response instances throughout emergencies by offering optimized routes to a location or by monitoring development employees’ or firefighters’ important indicators at life-threatening websites.
In healthcare, IoT offers suppliers the power to observe sufferers extra carefully utilizing an evaluation of the info that is generated. Hospitals typically use IoT techniques to finish duties equivalent to stock administration for each prescription drugs and medical devices.
Good buildings can, as an illustration, scale back power prices utilizing sensors that detect what number of occupants are in a room. The temperature can modify routinely — for instance, turning the air conditioner on if sensors detect a convention room is full or turning the warmth down if everybody within the workplace has gone residence.
In agriculture, IoT-based sensible farming techniques can assist monitor mild, temperature, humidity and soil moisture of crop fields utilizing related sensors. IoT can also be instrumental in automating irrigation techniques.
In a wise metropolis, IoT sensors and deployments, equivalent to sensible streetlights and sensible meters, can assist alleviate visitors, preserve power, monitor and handle environmental considerations and enhance sanitation.
IoT safety and privateness points
IoT connects billions of gadgets to the web and entails using billions of information factors, all of which should be secured. Resulting from its expanded assault floor, IoT safety and IoT privateness are cited as main considerations.
Some of the infamous IoT assaults occurred in 2016. The Mirai botnet infiltrated area title server supplier Dyn, leading to main system outages for an prolonged time frame. Attackers gained entry to the community by exploiting poorly secured IoT gadgets. That is one the biggest distributed denial-of-service assaults ever seen and Mirai continues to be being developed in the present day.
As a result of IoT gadgets are carefully related, a hacker can exploit one vulnerability to control all the info, rendering it unusable. Producers that do not replace their gadgets commonly — or in any respect — go away them susceptible to cybercriminals. Moreover, related gadgets typically ask customers to enter their private data, together with names, ages, addresses, cellphone numbers and even social media accounts — data that is invaluable to hackers.
Hackers aren’t the one menace to IoT; privateness is one other main concern. For instance, corporations that make and distribute shopper IoT gadgets might use these gadgets to acquire and promote consumer private information.
What’s the historical past of IoT?
Kevin Ashton, co-founder of the Auto-ID Heart on the Massachusetts Institute of Know-how (MIT), first talked about the web of issues in a presentation he made in 1999 to Procter & Gamble (P&G). Eager to convey radio frequency ID to the eye of P&G’s senior administration, Ashton referred to as his presentation “Internet of Things” to include the cool new pattern of 1999: the web. MIT professor Neil Gershenfeld’s guide, When Issues Begin to Suppose, additionally appeared in 1999. Though the guide did not use the precise time period, it offered a transparent imaginative and prescient of the place IoT was headed.
IoT has advanced from the convergence of wi-fi applied sciences, microelectromechanical techniques, microservices and the web. This convergence helped tear down the silos between operational know-how and data know-how, enabling unstructured machine-generated information to be analyzed for insights to drive enhancements.
Though Ashton’s was the primary point out of IoT, the thought of related gadgets has been round for the reason that Nineteen Seventies, underneath the monikers embedded web and pervasive computing.
The primary web equipment, for instance, was a Coke machine at Carnegie Mellon College within the early Nineteen Eighties. Utilizing the online, programmers might test the standing of the machine and decide whether or not there can be a chilly drink awaiting them, ought to they resolve to make the journey to the machine.
IoT advanced from M2M communication with machines connecting to one another by way of a community with out human interplay. M2M refers to connecting a tool to the cloud, managing it and amassing information.
Taking M2M to the following stage, IoT is a sensor community of billions of sensible gadgets that join individuals, laptop techniques and different functions to gather and share information. As its basis, M2M gives the connectivity that permits IoT.
IoT can also be a pure extension of supervisory management and information acquisition (SCADA), a class of software program software applications for course of management, the gathering of information in actual time from distant areas to manage gear and circumstances. SCADA techniques embrace {hardware} and software program elements. The {hardware} gathers and feeds information right into a desktop laptop that has SCADA software program put in, the place it is then processed and introduced in a well timed method. Late-generation SCADA techniques developed into first-generation IoT techniques.
The idea of the IoT ecosystem, nevertheless, did not actually come into its personal till 2010 when, partially, the federal government of China mentioned it will make IoT a strategic precedence in its five-year plan.
Between 2010 and 2019, IoT advanced with broader shopper use. Individuals more and more used internet-connected gadgets, equivalent to smartphones and sensible TVs, which have been all related to 1 community and will talk with one another.
In 2020, the variety of IoT gadgets continued to develop together with mobile IoT, which now labored on 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G in addition to LoRaWAN and long-term evolution for machines, or LTE-M.
In 2023, billions of internet-connected gadgets accumulate and share information for shopper and {industry} use. IoT has been an necessary facet within the creation of digital twins — which is a digital illustration of a real-world entity or course of.
The bodily connections between the entity and its twin are most frequently IoT sensors, and a well-configured IoT implementation is commonly a prerequisite for digital twins.
Likewise, IoT in healthcare has expanded in using wearables and in-home sensors that may remotely monitor a affected person’s well being.
Find out about 9 extra present and potential future tendencies in IoT.