The Idea of Diffusion
Denoising diffusion fashions are educated to drag patterns out of noise, to generate a fascinating picture. The coaching course of includes exhibiting mannequin examples of photos (or different knowledge) with various ranges of noise decided in response to a noise scheduling algorithm, desiring to predict what elements of the information are noise. If profitable, the noise prediction mannequin will be capable to step by step construct up a realistic-looking picture from pure noise, subtracting increments of noise from the picture at every time step.
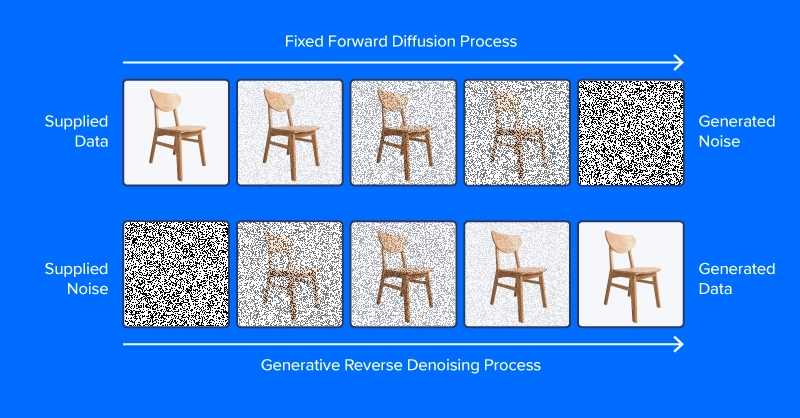
Not like the picture on the high of this part, trendy diffusion fashions don’t predict noise from a picture with added noise, a minimum of in a roundabout way. As an alternative, they predict noise in a latent house illustration of the picture. Latent house represents photos in a compressed set of numerical options, the output of an encoding module from a variational autoencoder, or VAE. This trick put the “latent” in latent diffusion, and enormously diminished the time and computational necessities for producing photos. As reported by the paper authors, latent diffusion hurries up inference by a minimum of ~2.7X over direct diffusion and trains about thrice quicker.
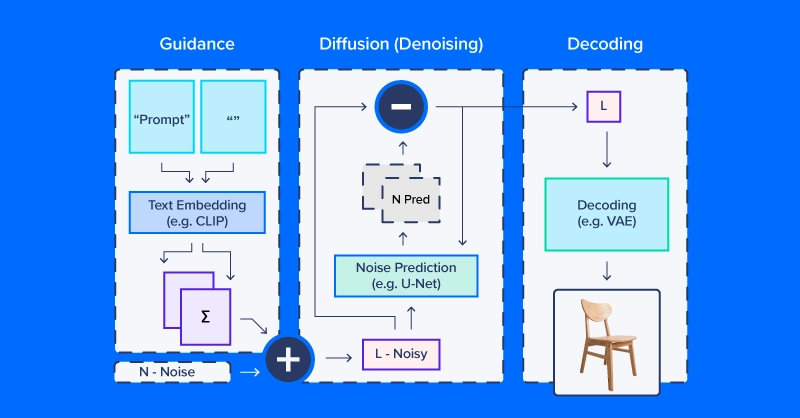
Folks working with latent diffusion typically discuss of utilizing a “diffusion model,” however the truth is, the diffusion course of employs a number of modules. As within the diagram above, a diffusion pipeline for text-to-image workflows sometimes features a textual content embedding mannequin (and its tokenizer), a denoise prediction/diffusion mannequin, and a picture decoder. One other necessary a part of latent diffusion is the scheduler, which determines how the noise is scaled and up to date over a collection of “time steps” (a collection of iterative updates that step by step take away noise from latent house).
Latent Diffusion Code Instance
We’ll use CompVis/latent-diffusion-v1-4 for many of our examples. Textual content embedding is dealt with by a CLIPTextModel and CLIPTokenizer. Noise prediction makes use of a ‘U-Net,’ a sort of image-to-image mannequin that initially gained traction as a mannequin for functions in biomedical photos (particularly segmentation). To generate photos from denoised latent arrays, the pipeline makes use of a variational autoencoder (VAE) for picture decoding, turning these arrays into photos.
We’ll begin by constructing our model of this pipeline from HuggingFace elements.
# native setup
virtualenv diff_env –python=python3.8
supply diff_env/bin/activate
pip set up diffusers transformers huggingface-hub
pip set up torch --index-url https://obtain.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
Ensure to test pytorch.org to make sure the fitting model on your system should you’re working domestically. Our imports are comparatively easy, and the code snippet under suffices for all the next demos.
import os
import numpy as np
import torch
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, AutoPipelineForImage2Image
from diffusers.pipelines.pipeline_utils import numpy_to_pil
from transformers import CLIPTokenizer, CLIPTextModel
from diffusers import AutoencoderKL, UNet2DConditionModel,
PNDMScheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler
from PIL import Picture
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Now for the main points. Begin by defining picture and diffusion parameters and a immediate.
immediate = [" "]
# picture settings
peak, width = 512, 512
# diffusion settings
number_inference_steps = 64
guidance_scale = 9.0
batch_size = 1
Initialize your pseudorandom quantity generator with a seed of your alternative for reproducing your outcomes.
def seed_all(seed):
torch.manual_seed(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
seed_all(193)
Now we are able to initialize the textual content embedding mannequin, autoencoder, a U-Internet, and the time step scheduler.
tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-large-patch14")
text_encoder = CLIPTextModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-large-patch14")
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
subfolder="vae")
unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
subfolder="unet")
scheduler = PNDMScheduler()
scheduler.set_timesteps(number_inference_steps)
my_device = torch.system("cuda") if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.system("cpu")
vae = vae.to(my_device)
text_encoder = text_encoder.to(my_device)
unet = unet.to(my_device)
Encoding the textual content immediate as an embedding requires first tokenizing the string enter. Tokenization replaces characters with integer codes equivalent to a vocabulary of semantic items, e.g. through byte pair encoding (BPE). Our pipeline embeds a null immediate (no textual content) alongside the textual immediate for our picture. This balances the diffusion course of between the supplied description and natural-appearing photos normally. We’ll see tips on how to change the relative weighting of those elements later on this article.
immediate = immediate * batch_size
tokens = tokenizer(immediate, padding="max_length",
max_length=tokenizer.model_max_length, truncation=True,
return_tensors="pt")
empty_tokens = tokenizer([""] * batch_size, padding="max_length",
max_length=tokenizer.model_max_length, truncation=True,
return_tensors="pt")
with torch.no_grad():
text_embeddings = text_encoder(tokens.input_ids.to(my_device))[0]
max_length = tokens.input_ids.form[-1]
notext_embeddings = text_encoder(empty_tokens.input_ids.to(my_device))[0]
text_embeddings = torch.cat([notext_embeddings, text_embeddings])
We initialize latent house as random regular noise and scale it in response to our diffusion time step scheduler.
latents = torch.randn(batch_size, unet.config.in_channels,
peak//8, width//8)
latents = (latents * scheduler.init_noise_sigma).to(my_device)
All the pieces is able to go, and we are able to dive into the diffusion loop itself. We will preserve observe of photos by sampling periodically all through so we are able to see how noise is step by step decreased.
photos = []
display_every = number_inference_steps // 8
# diffusion loop
for step_idx, timestep in enumerate(scheduler.timesteps):
with torch.no_grad():
# concatenate latents, to run null/textual content immediate in parallel.
model_in = torch.cat([latents] * 2)
model_in = scheduler.scale_model_input(model_in,
timestep).to(my_device)
predicted_noise = unet(model_in, timestep,
encoder_hidden_states=text_embeddings).pattern
# pnu - empty immediate unconditioned noise prediction
# pnc - textual content immediate conditioned noise prediction
pnu, pnc = predicted_noise.chunk(2)
# weight noise predictions in response to steering scale
predicted_noise = pnu + guidance_scale * (pnc - pnu)
# replace the latents
latents = scheduler.step(predicted_noise,
timestep, latents).prev_sample
# Periodically log photos and print progress throughout diffusion
if step_idx % display_every == 0
or step_idx + 1 == len(scheduler.timesteps):
picture = vae.decode(latents / 0.18215).pattern[0]
picture = ((picture / 2.) + 0.5).cpu().permute(1,2,0).numpy()
picture = np.clip(picture, 0, 1.0)
photos.prolong(numpy_to_pil(picture))
print(f"step {step_idx}/{number_inference_steps}: {timestep:.4f}")
On the finish of the diffusion course of, now we have a good rendering of what you needed to generate. Subsequent, we’ll go over further methods for higher management. As we’ve already made our diffusion pipeline, we are able to use the streamlined diffusion pipeline from HuggingFace for the remainder of our examples.
Controlling the Diffusion Pipeline
We’ll use a set of helper capabilities on this part:
def seed_all(seed):
torch.manual_seed(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
def grid_show(photos, rows=3):
number_images = len(photos)
peak, width = photos[0].measurement
columns = int(np.ceil(number_images / rows))
grid = np.zeros((peak*rows,width*columns,3))
for ii, picture in enumerate(photos):
grid[ii//columns*height:ii//columns*height+height,
ii%columns*width:ii%columns*width+width] = picture
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=(3*columns, 3*rows))
ax.imshow(grid / grid.max())
return grid, fig, ax
def callback_stash_latents(ii, tt, latents):
# tailored from fastai/diffusion-nbs/stable_diffusion.ipynb
latents = 1.0 / 0.18215 * latents
picture = pipe.vae.decode(latents).pattern[0]
picture = (picture / 2. + 0.5).cpu().permute(1,2,0).numpy()
picture = np.clip(picture, 0, 1.0)
photos.prolong(pipe.numpy_to_pil(picture))
my_seed = 193
We’ll begin with probably the most well-known and simple utility of diffusion fashions: picture technology from textual prompts, often known as text-to-image technology. The mannequin we’ll use was launched into the wild (of the Hugging Face Hub) by the tutorial lab that printed the latent diffusion paper. Hugging Face coordinates workflows like latent diffusion through the handy pipeline API. We need to outline what system and what floating level to calculate primarily based on if now we have or should not have a GPU.
if (1):
#Run CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 on GPU
pipe_name = "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
my_dtype = torch.float16
my_device = torch.system("cuda")
my_variant = "fp16"
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(pipe_name,
safety_checker=None, variant=my_variant,
torch_dtype=my_dtype).to(my_device)
else:
#Run CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 on CPU
pipe_name = "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
my_dtype = torch.float32
my_device = torch.system("cpu")
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(pipe_name,
torch_dtype=my_dtype).to(my_device)
Steering Scale
For those who use a really uncommon textual content immediate (very in contrast to these within the dataset), it’s potential to finish up in a less-traveled a part of latent house. The null immediate embedding offers a stability and mixing the 2 in response to guidance_scale means that you can commerce off the specificity of your immediate in opposition to widespread picture traits.
guidance_images = []
for steering in [0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, 6.0, 8.0, 10.0, 20.0]:
seed_all(my_seed)
my_output = pipe(my_prompt, num_inference_steps=50,
num_images_per_prompt=1, guidance_scale=steering)
guidance_images.append(my_output.photos[0])
for ii, img in enumerate(my_output.photos):
img.save(f"prompt_{my_seed}_g{int(guidance*2)}_{ii}.jpg")
temp = grid_show(guidance_images, rows=3)
plt.savefig("prompt_guidance.jpg")
plt.present()
Since we generated the immediate utilizing the 9 steering coefficients, you’ll be able to plot the immediate and think about how the diffusion developed. The default steering coefficient is 0.75 so on the seventh picture could be the default picture output.
Destructive Prompts
Typically latent diffusion actually “wants” to provide a picture that doesn’t match your intentions. In these eventualities, you should utilize a destructive immediate to push the diffusion course of away from undesirable outputs. For instance, we may use a destructive immediate to make our Martian astronaut diffusion outputs rather less human.
my_prompt = " "
my_negative_prompt = " "
output_x = pipe(my_prompt, num_inference_steps=50, num_images_per_prompt=9,
negative_prompt=my_negative_prompt)
temp = grid_show(output_x)
plt.present()
You must obtain outputs that comply with your immediate whereas avoiding outputting the issues described in your destructive immediate.
Picture Variation
Textual content-to-image technology from scratch is just not the one utility for diffusion pipelines. Really, diffusion is well-suited for picture modification, ranging from an preliminary picture. We’ll use a barely completely different pipeline and pre-trained mannequin tuned for image-to-image diffusion.
pipe_img2img = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained(
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", safety_checker=None,
torch_dtype=my_dtype, use_safetensors=True).to(my_device)
One utility of this method is to generate variations on a theme. An idea artist may use this system to shortly iterate completely different concepts for illustrating an exoplanet primarily based on the most recent analysis.
We’ll first obtain a public area artist’s idea of planet 1e within the TRAPPIST system (credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech).
Then, after downscaling to take away particulars, we’ll use a diffusion pipeline to make a number of completely different variations of the exoplanet TRAPPIST-1e.
url =
"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/38/TRAPPIST-1e_artist_impression_2018.png/600px-TRAPPIST-1e_artist_impression_2018.png"
img_path = url.break up("https://www.kdnuggets.com/")[-1]
if not (os.path.exists("600px-TRAPPIST-1e_artist_impression_2018.png")):
os.system(f"wget '{url}'")
init_image = Picture.open(img_path)
seed_all(my_seed)
trappist_prompt = "Artist's impression of TRAPPIST-1e"
"large Earth-like water-world exoplanet with oceans,"
"NASA, artist concept, realistic, detailed, intricate"
my_negative_prompt = "cartoon, sketch, orbiting moon"
my_output_trappist1e = pipe_img2img(immediate=trappist_prompt, num_images_per_prompt=9,
picture=init_image, negative_prompt=my_negative_prompt, guidance_scale=6.0)
grid_show(my_output_trappist1e.photos)
plt.present() 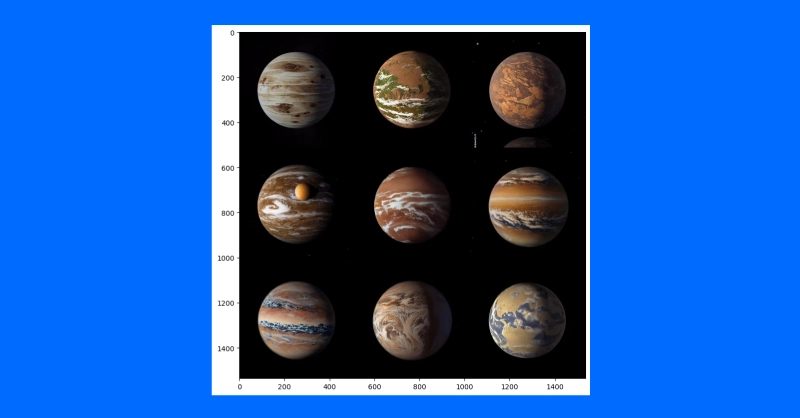
By feeding the mannequin an instance preliminary picture, we are able to generate related photos. It’s also possible to use a text-guided image-to-image pipeline to alter the type of a picture by rising the steering, including destructive prompts and extra similar to “non-realistic” or “watercolor” or “paper sketch.” Your mile might fluctuate and adjusting your prompts would be the best method to discover the fitting picture you need to create.
Conclusions
Regardless of the discourse behind diffusion techniques and imitating human generated artwork, diffusion fashions produce other extra impactful functions. It has been utilized to protein folding prediction for protein design and drug growth. Textual content-to-video can be an energetic space of analysis and is obtainable by a number of firms (e.g. Stability AI, Google). Diffusion can be an rising method for text-to-speech functions.
It’s clear that the diffusion course of is taking a central function within the evolution of AI and the interplay of expertise with the worldwide human surroundings. Whereas the intricacies of copyright, different mental property legal guidelines, and the impression on human artwork and science are evident in each optimistic and destructive methods. However what is really a optimistic is the unprecedented functionality AI has to know language and generate photos. It was AlexNet that had computer systems analyze a picture and output textual content, and solely now computer systems can analyze textual prompts and output coherent photos.
Authentic. Republished with permission.
Kevin Vu manages Exxact Corp weblog and works with a lot of its gifted authors who write about completely different elements of Deep Studying.
