A malware botnet known as Ebury is estimated to have compromised 400,000 Linux servers since 2009, out of which greater than 100,000 had been nonetheless compromised as of late 2023.
The findings come from Slovak cybersecurity agency ESET, which characterised it as one of the crucial superior server-side malware campaigns for monetary acquire.
“Ebury actors have been pursuing monetization activities […], including the spread of spam, web traffic redirections, and credential stealing,” safety researcher Marc-Etienne M.Léveillé mentioned in a deep dive evaluation.
“[The] operators are also involved in cryptocurrency heists by using AitM and credit card stealing via network traffic eavesdropping, commonly known as server-side web skimming.”
Ebury was first documented over a decade in the past as a part of a marketing campaign codenamed Operation Windigo that focused Linux servers to deploy the malware, alongside different backdoors and scripts like Cdorked and Calfbot to redirect net visitors and ship spam, respectively.
Subsequently, in August 2017, a Russian nationwide named Maxim Senakh was sentenced to almost 4 years in jail within the U.S. for his function within the improvement and upkeep of the botnet malware.
“Senakh and his co-conspirators used the Ebury botnet to generate and redirect internet traffic in furtherance of various click-fraud and spam email schemes, which fraudulently generated millions of dollars in revenue,” the U.S. Justice Division mentioned on the time.
“As part of his plea, Senakh admitted that he supported the criminal enterprise by creating accounts with domain registrars that helped develop the Ebury botnet infrastructure and personally profited from traffic generated by the Ebury botnet.”
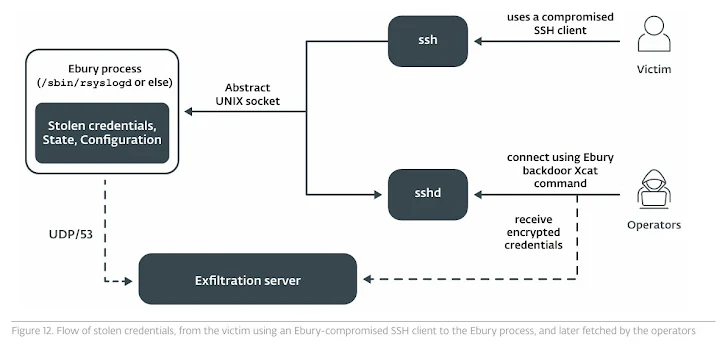
ESET’s investigation has unearthed varied approaches the attackers use to ship Ebury, together with strategies reminiscent of theft of SSH credentials, credential stuffing, infiltrating internet hosting supplier infrastructure, exploitation of flaws in Management Internet Panel (e.g., CVE-2021-45467), and SSH adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) assaults.
The risk actors have additionally been noticed utilizing faux or stolen identities to cowl their tracks, to not point out compromising infrastructure utilized by different perpetrators with the malware with a purpose to meet their targets and confuse attribution efforts.
“An example is the compromise of servers responsible for collecting data from Vidar Stealer,” ESET mentioned. “Ebury actors used the stolen identities obtained through Vidar Stealer for renting server infrastructure and in their activities, sending law enforcement bodies in the wrong directions.”
In one other occasion, Ebury is claimed to have been used to breach one of many Mirai botnet writer’s programs and steal the code a lot earlier than it was made public.
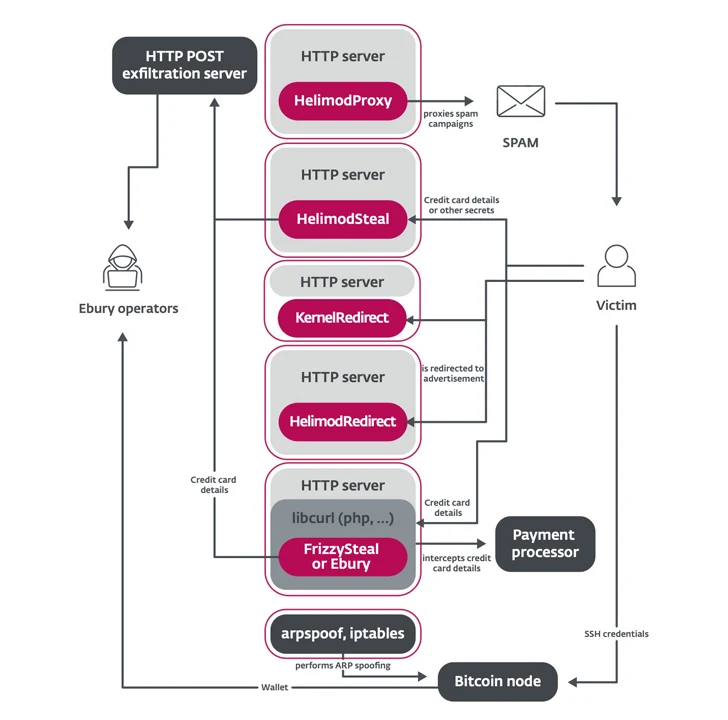
The malware acts each as a backdoor contained in the OpenSSH daemon and a credential stealer, providing attackers the power to deploy further payloads like HelimodSteal, HelimodRedirect, and HelimodProxy, and develop their presence inside a compromised community. The newest model of Ebury identified to this point is 1.8.2.
The up to date Ebury artifacts introduce new obfuscation strategies, a site era algorithm (DGA), and higher conceal its presence by functioning as a userland rootkit when injected contained in the shell of SSH classes.
“Those tools have the common goal of monetizing, through various methods, the servers they compromise,” ESET mentioned. “The way servers are monetized range from credit card information theft and cryptocurrency stealing to traffic redirection, spam sending, and credential stealing.”
HelimodSteal, HelimodRedirect, and HelimodProxy are all Apache HTTP server modules used for intercepting HTTP POST requests made to the net server, redirecting HTTP requests to advertisements, and proxying visitors to ship spam. One other new instrument employed is a kernel module known as KernelRedirect that implements a Netfilter hook to switch HTTP visitors to carry out redirection.
Additionally utilized are software program to cover and permit malicious visitors by means of the firewall, in addition to Perl scripts to hold out large-scale AitM assaults inside internet hosting suppliers’ knowledge facilities to breach useful targets and steal cryptocurrency from wallets hosted on these servers.
As many as 200 servers throughout greater than 75 networks in 34 totally different international locations are believed to have been focused on this method between February 2022 and Might 2023.
HelimodSteal can be designed to seize bank card knowledge that is submitted by a sufferer to a web-based retailer, successfully as a server-side net skimmer to extract the knowledge acquired by the contaminated server.
In an alternate chain of occasions, the monetary particulars could be obtained via Ebury or FrizzySteal, a malicious shared library that is injected into libcurl and might exfiltrate requests made by the compromised server to exterior HTTP servers, reminiscent of a cost processor.
“Since both are operating within the web server or application, end-to-end encryption (HTTPS) cannot protect against this threat,” ESET famous.
“Access to servers used for shared hosting grants them access to a lot of unencrypted web traffic, which they leverage for stealthy redirection or capturing details submitted in online forms.”