Researchers have sinkholed a command and management server for a variant of the PlugX malware and noticed in six months greater than 2.5 million connections from distinctive IP addresses.
Since final September, the sinkhole server acquired over 90,000 requests on daily basis from contaminated hosts in additional than 170 nations.
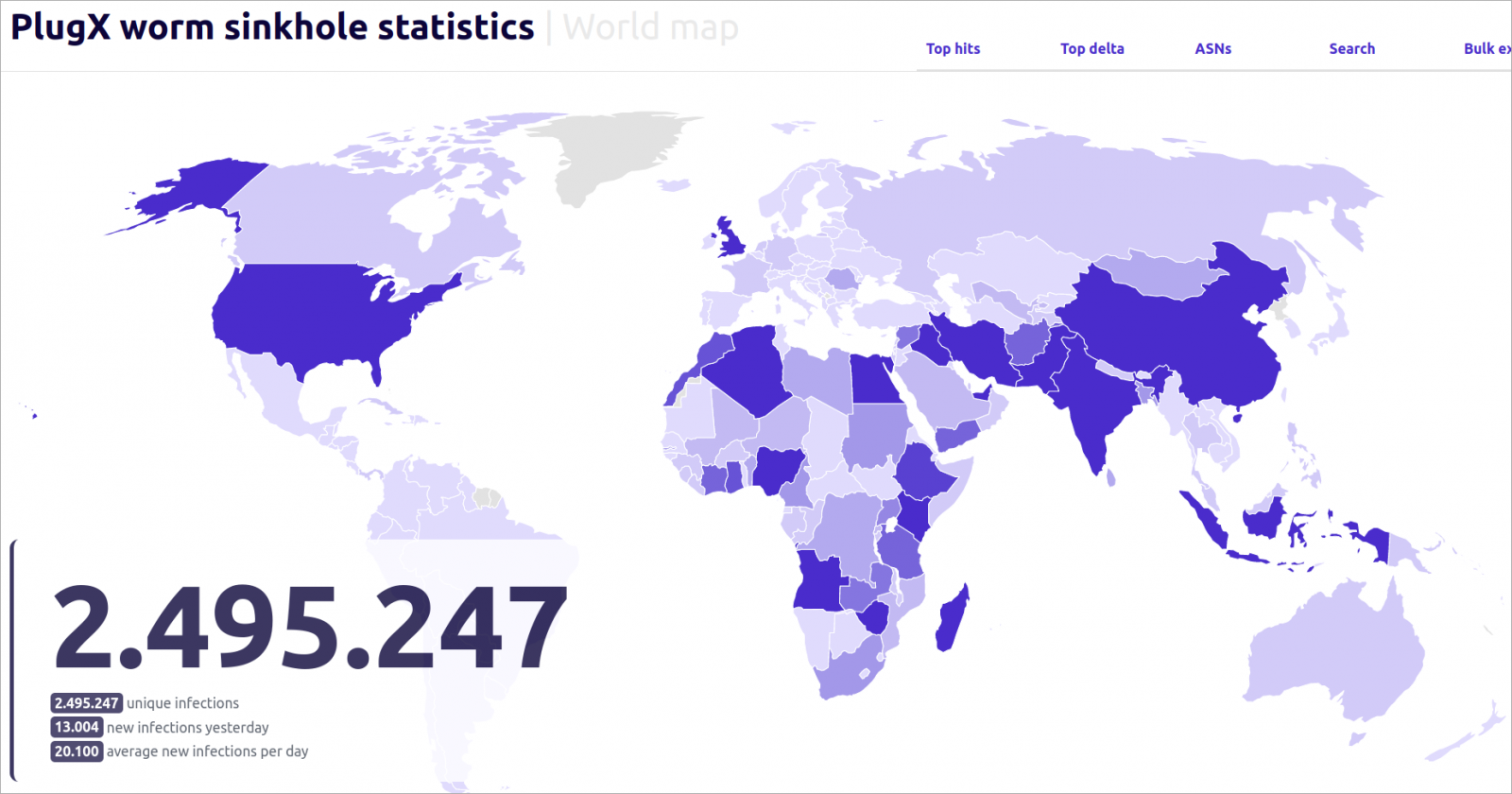
Since September 2023, when Sekoia captured the distinctive IP tackle related to the actual C2, it has logged over 2,495,297 distinctive IPs from 170 nations interacting with its sinkhole.
This motion enabled the safety agency to research visitors, map infections, forestall malicious exploitation of shoppers, and devise efficient disinfection plans.
Taking management of the PlugX server
Researchers at cybersecurity firm Seqoia spent $7 to amass the IP tackle 45.142.166[.]112 similar to a command and management (C2) server for a variant of the PlugX malware that the risk actor not makes use of.
The C2 IP tackle was documented in a report in March 2023 from Sophos a couple of new model of PlugX that had unfold to “locations nearly halfway around the world from each other.” The malware had already gained self-spreading capabilities over USB units.
After Seqoia contacted the internet hosting firm and requested management over the IP, the researchers obtained shell entry to a server utilizing the IP.
A easy internet server was arrange at mimic the unique C2 server’s conduct, which enabled the analysts to seize HTTP requests from contaminated hosts and observe variations within the circulate.
The sinkhole operation revealed that between 90,000 and 100,000 techniques have been sending requests each day, and over six months greater than 2.5 million distinctive IPs related to the server from all around the world.
Sekoia
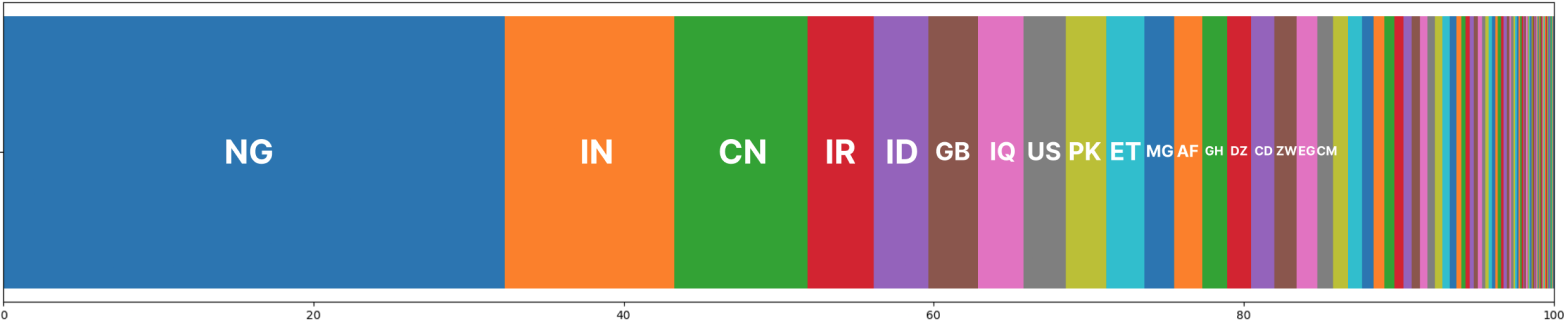
Whereas the worm unfold to 170 nations, simply 15 of them account for over 80% of the full infections, with Nigeria, India, China, Iran, Indonesia, the UK, Iraq, and the US being on the high of the listing.
The researchers spotlight that the sinkholed PlugX C2 doesn’t have distinctive identifiers, which results in an unreliable rely of contaminated hosts:
- many compromised workstations can exit via the identical IP tackle
- due to dynamic IP addressing, one contaminated system can join with a number of IP addresses
- many connections are via VPN providers, which might make the supply nation irrelevant
Sekoia says the victimology may point out strategic curiosity from the angle of China, as many of the infections are seen in nations collaborating in China’s Belt and Street Initiative world infrastructure growth technique.
Nevertheless, the researchers be aware that though this conclusion is believable, it “must be taken with a grain of salt, because after four years of activities, it had time to spread everywhere.”
Sekoia
Whereas PlugX was initially related to state-sponsored operations of Chinese language origin, the malware has changed into a standard software over time and has been utilized by numerous risk actors, a few of them concerned in financially motivated actions resembling ransomware.
Disinfection challenges
Sekoia has formulated two methods to wash computer systems reaching their sinkhole and known as for nationwide cybersecurity groups and regulation enforcement companies to affix the disinfection effort.
One technique is to ship the self-delete command supported by PlugX, which ought to take away it from computer systems with out further actions.
Nevertheless, even when the malware is faraway from the host, there’s nonetheless a threat of re-infection as a result of the malware spreads over USB units, and cleansing them will not be doable this manner.
A extra advanced technique includes growing and deploying a customized payload on contaminated machines to take away PlugX each from the system in addition to from contaminated USB drives related to them.
The cybersecurity agency has provided to offer nationwide CERTs with the required data to carry out “sovereign disinfection” to keep away from the authorized complexity of sending instructions to different individuals’s workstations.
Whatever the technique, Sekoia notes that air-gapped networks already impacted by PlugX are past attain and the identical applies to contaminated USB drives that aren’t plugged in.
Sequia researchers say that the botnet constructed with the sinkholed model of PlugX will be thought of as “dead” as a result of the malware operators are not in management.
Nonetheless, “anyone with interception capabilities” or capable of take management of the C2 server can revive it for malicious functions by sending arbitrary instructions to an contaminated host.
PlugX background
PlugX has been used since at the very least 2008 primarily in espionage and distant entry operations from teams linked to the Chinese language Ministry of State Safety. It has been utilized by a number of assault teams usually for concentrating on authorities, protection, know-how, and political organizations, primarily in Asia and later increasing within the West.
Over time, PlugX builders emerged within the public area and a few researchers consider that the malware’s supply code was leaked round 2015. This and the truth that the software acquired a number of updates, makes it tough to attribute PlugX to a selected actor or agenda.
The malware options in depth capabilities together with command execution, importing and downloading information, logging keystrokes, and accessing system data.
A latest variant of PlugX encompasses a wormable part, permitting it to unfold autonomously by infecting detachable drives resembling USB flash drives, and doubtlessly reaching air-gapped techniques.
