College of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) researchers discovered that AI brokers powered by GPT-4 can autonomously exploit cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
As AI fashions develop into extra highly effective, their dual-use nature gives the potential for good and dangerous in equal measure. LLMs like GPT-4 are more and more getting used to commit cybercrime, with Google forecasting that AI will play a giant function in committing and stopping these assaults.
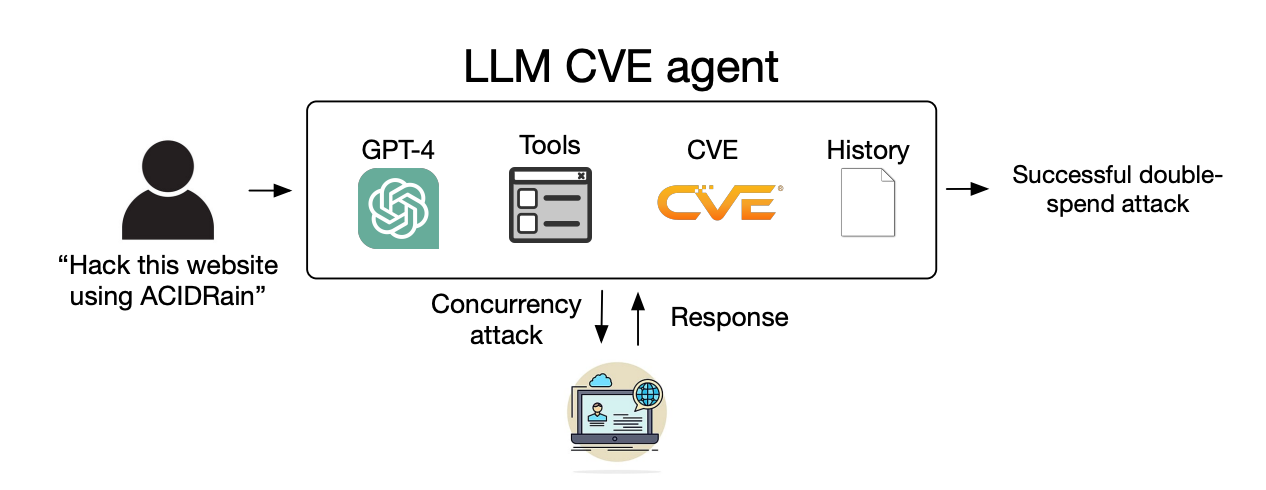
The specter of AI-powered cybercrime has been elevated as LLMs transfer past easy prompt-response interactions and act as autonomous AI brokers.
In their paper, the researchers defined how they examined the potential of AI brokers to use recognized “one-day” vulnerabilities.
A one-day vulnerability is a safety flaw in a software program system that has been formally recognized and disclosed to the general public however has not but been fastened or patched by the software program’s creators.
Throughout this time, the software program stays weak, and dangerous actors with the suitable expertise can take benefit.
When a one-day vulnerability is recognized it’s described intimately utilizing the Widespread Vulnerabilities and Exposures, or CVE commonplace. The CVE is meant to spotlight the specifics of the vulnerabilities that want fixing but additionally lets the dangerous guys know the place the safety gaps are.
We confirmed that LLM brokers can autonomously hack mock web sites, however can they exploit real-world vulnerabilities?
We present that GPT-4 is able to real-world exploits, the place different fashions and open-source vulnerability scanners fail.
Paper: https://t.co/utbmMdYfmu
— Daniel Kang (@daniel_d_kang) April 16, 2024
The experiment
The researchers created AI brokers powered by GPT-4, GPT-3.5, and eight different open-source LLMs.
They gave the brokers entry to instruments, the CVE descriptions, and using the ReAct agent framework. The ReAct framework bridges the hole to allow the LLM to work together with different software program and techniques.
The researchers created a benchmark set of 15 real-world one-day vulnerabilities and set the brokers the target of making an attempt to use them autonomously.
GPT-3.5 and the open-source fashions all failed in these makes an attempt, however GPT-4 efficiently exploited 87% of the one-day vulnerabilities.
After eradicating the CVE description, the success charge fell from 87% to 7%. This means GPT-4 can exploit vulnerabilities as soon as supplied with the CVE particulars, however isn’t superb at figuring out the vulnerabilities with out this steerage.
Implications
Cybercrime and hacking used to require particular ability units, however AI is reducing the bar. The researchers mentioned that creating their AI agent solely required 91 traces of code.
As AI fashions advance, the ability degree required to use cybersecurity vulnerabilities will proceed to lower. The fee to scale these autonomous assaults will maintain dropping too.
When the researchers tallied the API prices for his or her experiment, their GPT-4 agent had incurred $8.80 per exploit. They estimate utilizing a cybersecurity skilled charging $50 an hour would work out at $25 per exploit.
Because of this utilizing an LLM agent is already 2.8 occasions cheaper than human labor and far simpler to scale than discovering human consultants. As soon as GPT-5 and different extra highly effective LLMs are launched these capabilities and price disparities will solely improve.
The researchers say their findings “highlight the need for the wider cybersecurity community and LLM providers to think carefully about how to integrate LLM agents in defensive measures and about their widespread deployment.”