Russian hacker group Sandworm aimed to disrupt operations at round 20 vital infrastructure amenities in Ukraine, based on a report from the Ukrainian Pc Emergency Response Workforce (CERT-UA).
Also called BlackEnergy, Seashell Blizzard, Voodoo Bear, and APT44, the hackers are believed to be related to Russia’s Primary Directorate of the Basic Employees of the Armed Forces (the GRU), finishing up cyberespionage and damaging assaults on numerous targets.
CERT-UA stories that in March 2024, APT44 carried out operations to disrupt info and communication techniques at power, water, and heating suppliers in 10 areas of Ukraine.
The assaults occurred in March and in some instances the hackers have been in a position to infiltrate the focused community by poisoning the availability chain to ship compromised or weak software program, or by the software program supplier’s means to entry group’s techniques for upkeep and technical assist.
Sandworm additionally mixed beforehand documented malware with new malicious instruments (BIASBOAT and LOADGRIP for Linux) to acquire entry and transfer laterally on the community.
CERT-UA specialists have confirmed the compromise of not less than three “supply chains,” because of which the circumstances of the preliminary unauthorized entry both correlate with the set up of software program containing backdoors and vulnerabilities or are brought on by the common technical means of the provider staff to entry the organizations’ ICS for upkeep and technical assist. – CERT-UA (machine translated).
The Ukrainian company notes that Sandworm’s breaches have been made simpler by the targets’ poor cybersecurity practices (e.g. lack of community segmentation and inadequate defenses on the software program provider stage).
From March 7 to March 15, 2024, CERT-UA engaged in intensive counter-cyberattack operations, which included informing affected enterprises, eradicating malware, and enhancing safety measures.
Primarily based on the findings from investigating the logs retrieved from the compromised entities, Sandworm relied on the next malware for its assaults on Ukraine’s utility suppliers:
- QUEUESEED/IcyWell/Kapeka: C++ backdoor for Home windows that collects fundamental system info and executes instructions from a distant server. It handles file operations, command execution, and configuration updates and might delete itself. Communications are secured by way of HTTPS, and information is encrypted utilizing RSA and AES. It shops its information and maintains persistence on contaminated techniques by encrypting its configuration within the Home windows registry and establishing duties or registry entries for computerized execution.
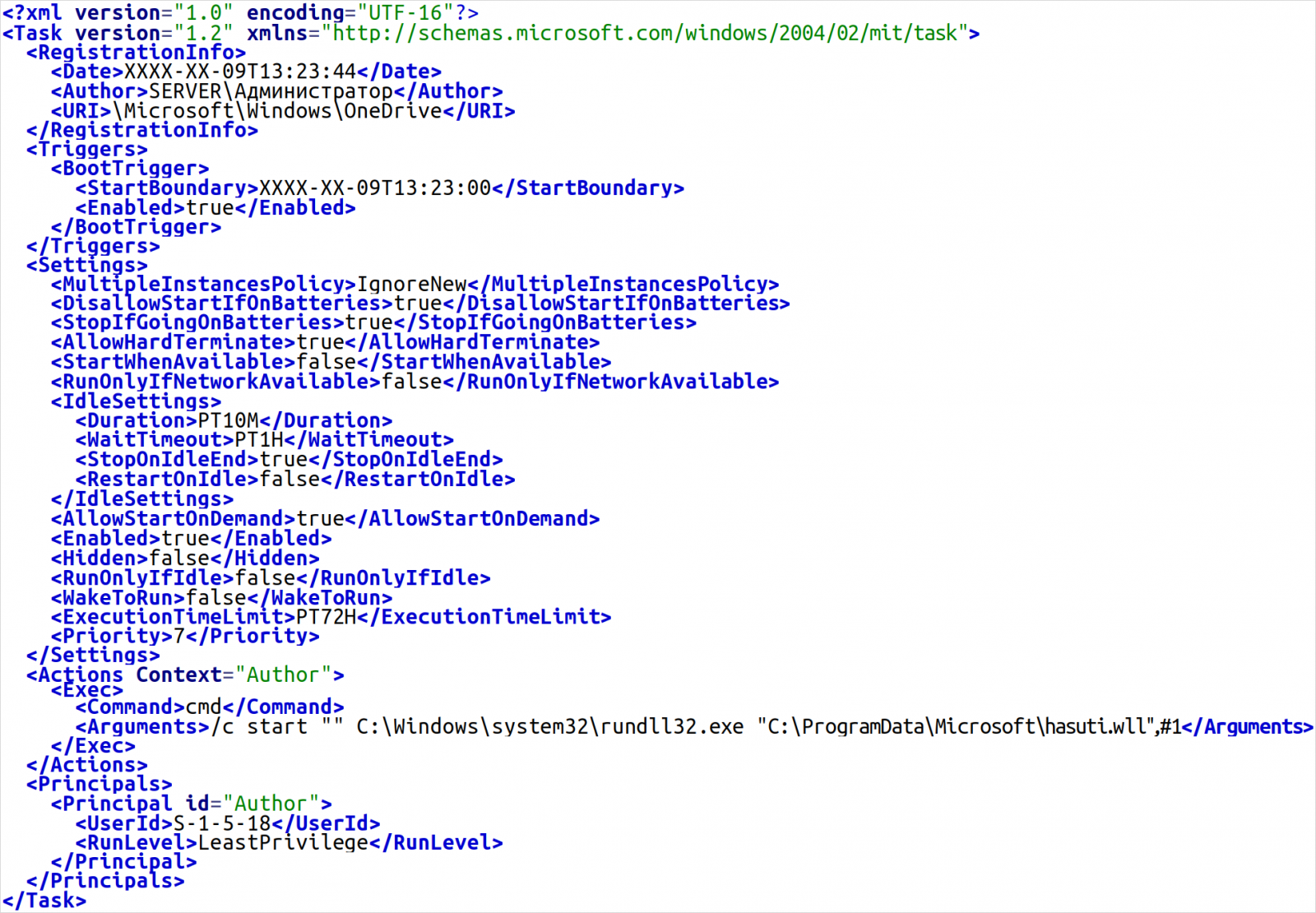
- BIASBOAT (new): a Linux variant of QUEUESEED that emerged lately. It’s disguised as an encrypted file server and operates alongside LOADGRIP.
- LOADGRIP (new): additionally a Linux variant of QUEUESEED developed in C, used to inject a payload into processes utilizing the ptrace API. The payload is often encrypted, and the decryption secret’s derived from a relentless and a machine-specific ID.
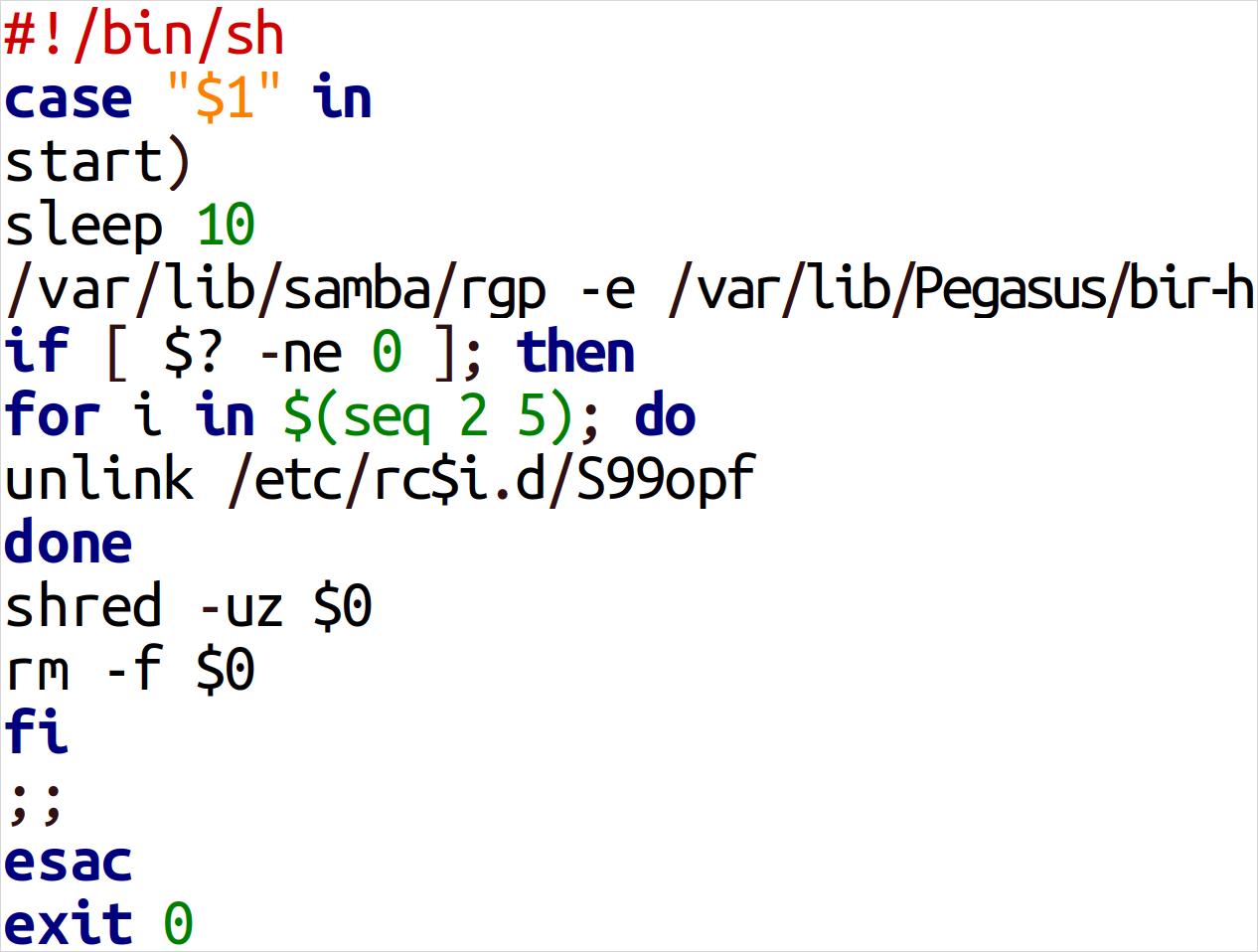
- GOSSIPFLOW: Go-based malware use on Home windows to set up tunneling utilizing the Yamux multiplexer library; it supplies SOCKS5 proxy performance to assist exfiltrate information and safe communication with the command and management server.
Further malicious instruments CERT-UA found throughout the investigation are from the open supply area and embody the Weevly webshell, the Regeorg.Neo, Pitvotnacci, and Chisel tunnelers, LibProcessHider, JuicyPotatoNG, and RottenPotatoNG.
The menace actors used these instruments to keep up persistence, conceal malicious processes, and elevate their privileges on compromised techniques.
The Ukrainian company belives that the aim of those assaults was to extend the impact of Russian missile strikes on the focused infrastructure amenities.
Final week, Mandiant uncovered Sandworm’s connection to a few hacktivist-branded Telegram teams which have beforehand claimed assaults on vital infrastructure in Europe and the U.S.
CERT-UA’s report supplies an extended listing of indicators of compromise that features information, hosts, and community particulars.