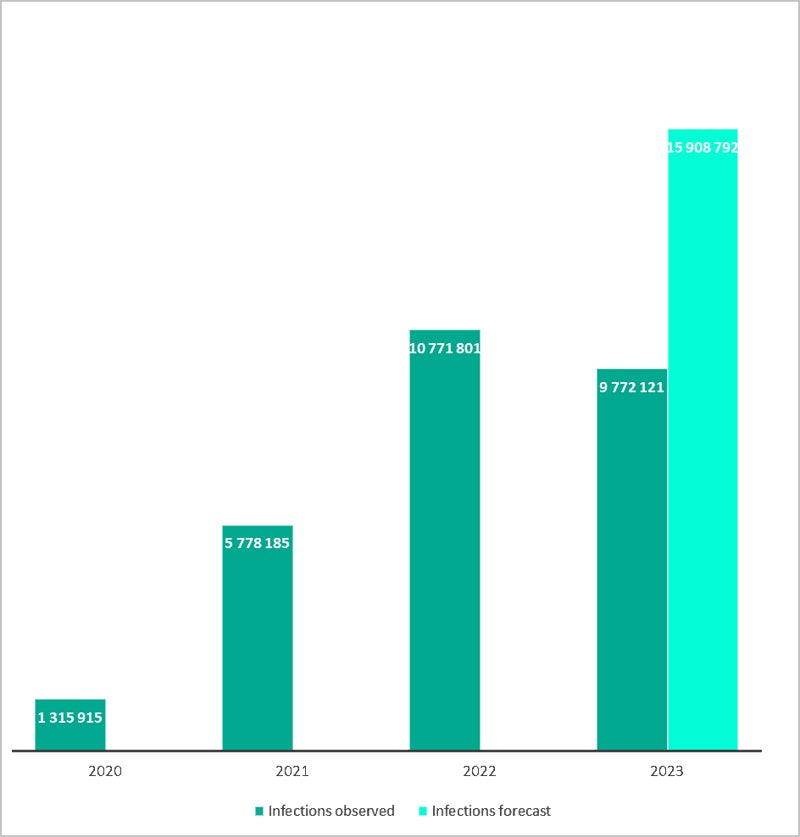
The variety of gadgets contaminated with data-stealing malware in 2023 was 9.8 million, a sevenfold improve over the identical determine for 2020, in keeping with new analysis from Kaspersky Digital Footprint Intelligence. Nonetheless, the researchers consider that the true determine could possibly be as excessive as 16 million, as credentials from gadgets contaminated in 2023 might not be leaked onto the darkish net till later this 12 months (Determine A).
Cybercriminals stole a median of fifty.9 credentials per compromised machine, and 443,000 web sites have had person info leaked prior to now 5 years.
The info was obtained from log information that document the actions of “infostealers.” Infostealers are a sort of malware that covertly extracts information from contaminated gadgets with out encrypting it. These logfiles are “actively traded in underground markets” and monitored by Kaspersky as a part of its digital danger safety service.
Sergey Shcherbel, professional at Kaspersky Digital Footprint Intelligence, mentioned in a press launch, “Leaked credentials carry a major threat, enabling cybercriminals to execute various attacks such as unauthorized access for theft, social engineering or impersonation.”
Why is the variety of data-stealing malware instances rising?
Infostealers are extra accessible
In keeping with a report by IBM, there was a 266% improve in infostealing malware in 2023 over the earlier 12 months. It seems to be efficient, too, as incidences of criminals gaining entry through the use of legitimate login credentials went up by 71%.
The recognition of infostealers is extensively regarded to be linked to the growing worth of company information and the malware’s rising accessibility. In separate analysis, Kaspersky Digital Footprint Intelligence discovered that 24% of malware bought as a service between 2015 and 2022 was infostealers, which permit beginner cybercriminals to make the most of infostealers developed by one other group and distributed through the darkish net.
Luke Stevenson, cyber safety product supervisor at managed service supplier Redcentric, advised TechRepublic in an e mail, “Stealer malware considerably lowers the entry barrier to would-be cyber criminals, making information breaches simpler. Exfiltrated information has rapid worth no matter the direct sufferer’s monetary assets and could be bought on rapidly throughout the vary of illicit legal boards.
“The malware is relatively easy to compile and deploy with source codes accessible for those starting out. Unlike ransomware which has its own business ecosystem, those operating infostealers generally have much lower overhead costs.”
Aamil Karimi, menace intelligence chief at cybersecurity agency Optiv, advised TechRepublic in an e mail, “There was a notable rise in new stealer malware introduced to the cybercriminal ecosystem beginning in 2019, including very popular strains like RedLine, Lumma and Raccoon. Some of these stealer malware variants have been used in ransomware operations that have shown increased activity over the last few years. These variants are very inexpensive, and they have proven to work, so there is incentive for more potential criminals to join these malware-as-a-service operations and affiliate programs.”
Moreover, the proliferation of “dedicated leak sites,” the place stolen credentials are posted, gives extra targets for infostealers. The extra websites of this nature are energetic — and the quantity grew by 83%, in keeping with Group-IB’s Hello-Tech Crime Developments 2022/2023 report — the upper the danger that corporations could have their gadgets compromised. Analysis from Group-IB revealed the variety of corporations that had their information uploaded to leak websites in 2023 elevated by 74% over the earlier 12 months.
Provide chains have gotten extra advanced and weak
Another excuse that data-stealing malware instances are rising is because of the provide chain. Third-party distributors are sometimes given entry to inner information or use linked techniques and will present a neater entry level that results in confidential information belonging to the goal group.
Dr. Stuart Madnick, an IT professor and cybersecurity researcher on the Massachusetts Institute of Expertise, wrote within the Harvard Enterprise Evaluation, “Most corporations have elevated the cyber safety of their ‘front doors’ by way of measures resembling firewalls, stronger passwords, multi-factor identification, and such. So, attackers search different — and typically extra harmful — methods to get it. Usually, which means coming in through distributors’ techniques.
“Most corporations depend on distributors to help them, from doing air-con upkeep to offering software program, together with automated updates to that software program. As a way to present these companies, these distributors want easy accessibility to your organization’s techniques — I refer to those because the ‘side doors.’ However, these distributors are regularly small corporations with restricted cybersecurity assets.
“Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in these vendor systems. Once they have some control over these vendor systems, they can use the side door to get into the systems of their customers.”
Analysis from the Financial institution for Worldwide Settlements means that international provide chains have gotten longer and extra advanced, which will increase the variety of potential entry factors for attackers. A report from the Id Theft Useful resource Middle discovered that the variety of organizations impacted by provide chain assaults surged by greater than 2,600 proportion factors between 2018 and 2023.
Malware sorts are growing in quantity
The quantity of malware accessible to cybercriminals is growing exponentially, in keeping with Optiv’s senior malware analyst McKade Ivancic, facilitating extra data-stealing assaults. He advised TechRepublic in an e mail, “The more that stealer-family malware is authored, the more those families’ code bases will be pilfered and re-written into similar, yet slightly different, data-stealers.”
He added, “Security teams, products, signatures and the like cannot grow exponentially like malware can. Until a more permanent solution is found, the ‘good guys’ will be naturally outpaced due to sheer numbers, compound growth, ease of access, lack of enforcement and attack surface expansion via growing technology and software investments.”
WFH and BYOD fashions are extra commonplace
Karimi advised TechRepublic, “The increase in the work-from-home and bring-your-own-device models since 2020 also likely contributed to increased risk to companies whose employees’ devices were not centrally or responsibly managed.”
Private gadgets are likely to lack the identical safety measures as company-provided gadgets, creating a bigger assault floor for criminals trying to deploy data-stealing malware. Microsoft’s Digital Protection Report 2023 acknowledged that as much as 90% of ransomware assaults in 2023 originated from unmanaged or bring-your-own gadgets.
What sort of credentials do cybercriminals goal?
The credentials typically focused by attackers utilizing data-stealing malware are those who may result in precious information, cash or privileged entry. Such particulars could embody company logins for emails or inner techniques, in addition to social media, on-line banking or cryptocurrency wallets, in keeping with the Kaspersky analysis.
SEE: Kaspersky’s Superior Persistent Threats Predictions for 2024
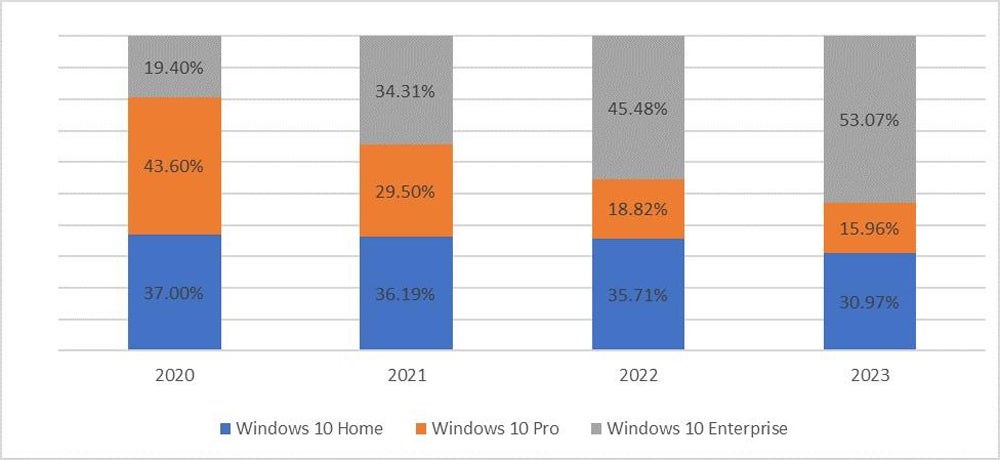
One other research by the agency discovered that over half (53%) of gadgets contaminated with data-stealing malware in 2023 had been company. This conclusion was drawn from the truth that the vast majority of contaminated gadgets with Home windows 10 software program are particularly operating Home windows 10 Enterprise (Determine B).
How a lot information could be extracted with data-stealing malware?
Every log file analyzed by Kaspersky Digital Footprint Intelligence on this research contained account credentials for a median of 1.85 company net purposes, together with emails, inner portals and buyer information processing techniques. Because of this criminals are sometimes capable of entry a number of accounts, each enterprise and private, after infecting a single machine.
The log file information additionally revealed {that a} fifth of workers would reopen the malware on their machine greater than as soon as, giving the cybercriminals entry to their information on a number of events with out the necessity for reinfection.
Shcherbel mentioned within the press launch, “This may indicate several underlying issues, including insufficient employee awareness, ineffective incident detection and response measures, a belief that changing the password is sufficient if the account has been compromised and a reluctance to investigate the incident.”
What do cybercriminals do with the stolen information?
In keeping with Kaspersky Digital Footprint Intelligence, menace actors will use the credentials stolen from malware-infected gadgets for numerous functions. These embody:
- Perpetrating cyberattacks on different events.
- Promoting them to others on the darkish net or shadow Telegram channels.
- Leaking them at no cost to sabotage a company or higher their very own fame.
Shcherbel mentioned within the press launch, “The dark-web worth of log information with login credentials varies relying on the information’s enchantment and the way in which it’s bought there.
“Credentials could also be bought by way of a subscription service with common uploads, a so-called ‘aggregator’ for particular requests, or through a ‘shop’ promoting not too long ago acquired login credentials solely to chose consumers. Costs sometimes start at $10 per log file in these outlets.
“This highlights how crucial it is both for individuals and companies – especially those handling large online user communities – to stay alert.”
How can companies shield themselves from data-stealing malware?
To protect towards data-stealing malware, researchers at Kaspersky Digital Footprint Intelligence really helpful the next:
- Monitor darkish net markets for compromised accounts related to the corporate.
- Change the passwords of compromised accounts and monitor them for suspicious exercise.
- Advise probably contaminated workers to run antivirus software program on all gadgets and take away any malware.
- Set up safety options on firm gadgets that alert customers to risks like suspicious websites or phishing emails.
TechRepublic consulted different consultants for added recommendation.
Encryption and entry controls
Matthew Corwin, managing director at cybersecurity agency Guidepost Options, advised TechRepublic in an e mail: “Encryption of data both at rest and in transit is critical for preventing data-stealing and exposure attacks, but for this to be effective a comprehensive defense-in-depth security architecture around the encrypted assets is also required.”
Stevenson added that “securing accounts via password managers and multi-factor authentication” is a crucial fundamental step for safeguarding account credentials from unauthorized use.
SEE: 6 Finest Open-Supply Password Managers for Home windows in 2024
Danger assessments
Corwin advised TechRepublic, “Periodic security and risk assessments can help identify specific weaknesses in an organization’s security posture which could be exploited by threat actors using data-stealing malware.”
Schooling
Karimi advised TechRepublic, “Creating a extra proactive method to danger administration requires training and consciousness — each for the IT staff and safety directors, in addition to customers usually.
“Security awareness is often touted as a default recommendation, but risk awareness is not. It is more comprehensive than a single online security awareness training module… It is important to establish processes to identify and track the most relevant threats that are unique to your environment.”
He added that “drafting, updating and enforcing business use cases and user policies for web activity” can present further safety assurance by making certain all employees are dealing with their credentials safely.