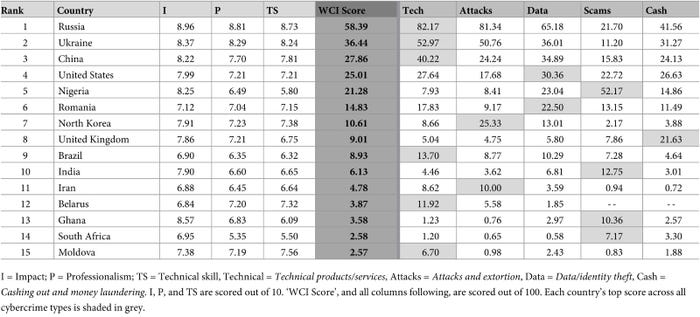
An educational analysis venture to realize perception into which nations produce essentially the most cybercrime has ranked the same old suspects of Russia, Ukraine, China, and the USA on the very prime but in addition discovered some relative surprises with Nigeria at No. 5, Romania at No. 6, and Brazil at No. 9.
Nations with excessive expertise ranges usually scored pretty excessive on the World Cybercrime Index (WCI), particularly if these international locations even have state-sponsored risk actors that overlap with cybercriminal teams. But different nations dominated in one of many 5 areas, corresponding to Nigeria taking the highest rating for scams and Romania scoring extremely in knowledge and identification theft, based on the college analysis effort by tutorial establishments in the UK, Australia, and France.
Whereas cybersecurity consultants have lengthy related totally different international locations with various kinds of cybercrime — Russia with banking and ransomware and China with intellectual-property theft and monetary crimes, for instance — that is the primary time that researchers have been in a position to evaluate varied international locations primarily based on particular attributes and cybercriminal approaches, says Miranda Bruce, a postdoctoral fellow in sociology on the College of Oxford.
“If you look closely at these five indices, you’ll get more insight into the character of each country as a cybercrime hotspot,” she says. “Nigeria is No. 1 in the Scams index, but comes between 5th and 10th in the other four cybercrime types. Clearly they’re a significant producer of all types of cybercrime, but it’s also clear that, as a country, they specialize.”
The researchers collected survey knowledge from 92 cybercrime consultants, asking them to choose the highest 5 cybercrime-producing nations in 5 totally different classes of crime: technical services; assaults and extortion; knowledge and identification theft; scams; and cashing out or cash laundering. For every nation, contributors had been requested to price the nation on the affect of the crimes, the actors’ professionalism, and their technical ability.
The highest 15 nations as ranked by their general World Cybercrime Index. Supply: PLOS One
In all, the cybercrime consultants nominated 97 totally different international locations, based on a paper the group revealed within the journal PLOS One.
The WCI scores might not, nonetheless, discern between true cybercriminals residing in a nation and people mercenary teams that additionally conduct operations on behalf of their state sponsors, says Sean McNee, vp of analysis and knowledge at DomainTools, a website safety providers agency.
“When evaluating cybercrime groups in locales such as Russia, China, Iran, or North Korea, it is always challenging to determine if groups are operating purely on their own accord or operating on behalf of a nation-state sponsor,” McNee says. “This makes cybercrime actors in other countries more interesting to look into, such as Nigeria, India, and Brazil.”
Low Technical Rating, Excessive Risk
Nigeria’s prime marks within the scams class — by which the researchers lumped collectively advance-fee fraud, enterprise e-mail compromise, and on-line public sale fraud — underscore {that a} extremely developed cybercrime ecosystem doesn’t essentially require important depth of technical abilities and infrastructure. Whereas Nigeria has prioritized its cybersecurity capabilities, the nation stays a bastion for e-mail fraud, as demonstrated by the case of a Nigerian-based group conducting romance scams with a US-based nationwide, who was sentenced earlier this yr.
Romania, which ranked No. 6 on the checklist, has an extended historical past of internet hosting a cybercriminal ecosystem, so its rating is a little bit of a shock, says Chester Wisniewski, director and discipline CTO at cybersecurity agency Sophos.
“Romania has always had elevated cybercrime activity … likely due to its well-educated population and proximity and relationships with neighboring cybercrime states like Ukraine, Russia, and Moldova,” he says. “Romania has been cooperative with cybercrime takedowns, but I am not sure they are very proactive in nature.”
The researchers plan to research how the World Cybercrime Index correlates with different traits of every nation — corresponding to gross home product (GDP), earnings inequality, Web penetration, and corruption — and the way cybercrime insurance policies can affect their scores, the College of Oxford’s Bruce says.
“There’s still much to learn about how and why countries like Russia, China, and the USA have become major cybercrime hotspots, but the countries that appear lower in the Index will tell us more about the nuances of cyber criminality,” she says. “That is, the specific combination of factors that enable a region to become a thriving economic hub of cybercriminal activity. It’s important that we pay attention to these countries and regions in the coming years.”
Room for Enchancment
Sadly, the information provides little actionable info to defenders, though it may very well be helpful to policymakers and diplomats considering influencing international locations and gaining cooperation, says Sophos’ Wisniewski.
“If these stats are accurate, only the countries listed are in a position to address the problem of them being a source country for cybercrime,” he says. “Many of those listed might not only be uninterested in reducing their rank, but they may also be proud of it.”
The researchers performed the survey in 2021, so sadly, that implies that the rankings have aged, and don’t embody main adjustments to the cyberthreat panorama, corresponding to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the latest rise in romance scams, and a rise in cryptocurrency scams from North Korea, says DomainTools’ McNee.
“This suggests that encouraging policies to promote technology sectors in these countries — turn cybercriminals to entrepreneurs — could have a net positive impact on the economy,” he says. “It may be more beneficial to track these trends in countries further down the WCI to help encourage such policies before a notable cybercrime industry takes hold.”