A brand new variant of the Mirai-based botnet malware Aquabot has been noticed actively exploiting CVE-2024-41710, a command injection vulnerability in Mitel SIP telephones.
The exercise was found by Akamai’s Safety Intelligence and Response Staff (SIRT), who stories that that is the third variant of Aquabot that falls below their radar.
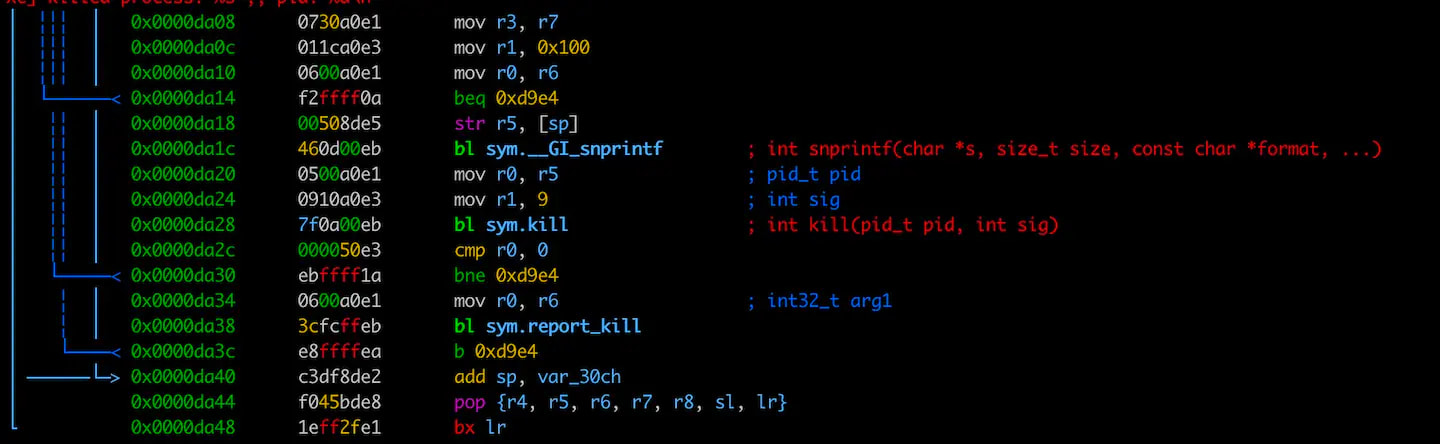
The malware household was launched in 2023, and a second model that added persistence mechanisms was launched later. The third variant, ‘Aquabotv3,’ launched a system that detects termination alerts and sends the information to the command-and-control (C2) server.
Akamai feedback that Aquabotv3’s mechanism to report again kill makes an attempt is uncommon for botnets and will have been added to present its operators higher monitoring.
Supply: Akamai
Focusing on Mitel telephones
CVE-2024-41710 is a command injection flaw impacting Mitel 6800 Collection, 6900 Collection, and 6900w Collection SIP Telephones, sometimes utilized in company places of work, enterprises, authorities companies, hospitals, academic institutes, resorts, and monetary establishments.
It’s a medium-severity flaw that permits an authenticated attacker with admin privileges to conduct an argument injection assault because of inadequate parameter sanitization through the boot course of, leading to arbitrary command execution.
Mitel launched fixes and a safety advisory about this flaw on July 17, 2024, urging customers to improve. Two weeks later, safety researcher Kyle Burns revealed a proof-of-concept (PoC) on GitHub.
Aquabotv3’s use of this PoC to use CVE-2024-41710 in assaults is the primary documented case of leveraging this vulnerability.
“Akamai SIRT detected exploit attempts targeting this vulnerability through our global network of honeypots in early January 2025 using a payload almost identical to the PoC,” explains the researchers.
The truth that the assaults require authentication signifies that the malware botnet makes use of brute-forcing to achieve preliminary entry.
The attackers craft an HTTP POST request focusing on the weak endpoint 8021xsupport.html, liable for 802.1x authentication settings in Mitel SIP telephones.
The applying improperly processes consumer enter, permitting malformed information to be inserted into the cellphone’s native configuration (/nvdata/and so forth/native.cfg).
By way of the injection of line-ending characters (%dt → %0d), attackers obtain manipulation of how the configuration file is parsed throughout system boot to execute a distant shell script (bin.sh) from their server.
This script downloads and installs an Aquabot payload for the outlined structure (x86, ARM, MIPS, and so forth), units its execution permissions utilizing ‘chmod 777,’ after which cleans up any traces.
Aquabotv3 exercise
As soon as persistence is ensured, Aquabotv3 connects to its C2 through TCP to obtain directions, assault instructions, updates, or extra payloads.
Subsequent, it makes an attempt to unfold to different IoT units utilizing the Mitel exploit, CVE-2018-17532 (TP-Hyperlink), CVE-2023-26801 (IoT firmware RCE), CVE-2022-31137 (Internet App RCE), Linksys E-series RCE, Hadoop YARN, and CVE-2018-10562 / CVE-2018-10561 (Dasan router bugs).
The malware additionally makes an attempt to brute pressure default or weak SSH/Telnet credentials to unfold to poorly secured units on the identical community.
The objective of Aquabotv3 is to enlist units on its distribution denial of service (DDoS) swarm and use them to hold out TCP SYN, TCP ACK, UDP, GRE IP, and application-layer assaults.
The botnet’s operator advertises its DDoS capabilities on Telegram below the names Cursinq Firewall, The Eye Companies, and The Eye Botnet, presenting it as a testing software for DDoS mitigation measures.
Akamai has listed the indications of compromise (IoC) related to Aquabotv3, in addition to Snort and YARA guidelines for detecting the malware, on the backside of its report.
