A workforce of researchers from New York College has made progress in neural speech decoding, bringing us nearer to a future by which people who’ve misplaced the power to talk can regain their voice.
The research, revealed in Nature Machine Intelligence, presents a novel deep studying framework that precisely interprets mind indicators into intelligible speech.
Folks with mind accidents from strokes, degenerative situations, or bodily trauma may be capable of use such units to talk utilizing voice synthesizers based mostly on their ideas alone.
It includes a deep studying mannequin that maps electrocorticography (ECoG) indicators to a set of interpretable speech options, similar to pitch, loudness, and the spectral content material of speech sounds.
ECoG information captures the important parts of speech manufacturing and permits the system to generate a compact illustration of the supposed speech.
The second stage includes a neural speech synthesizer that converts the extracted speech options into an audible spectrogram, which may then be reworked right into a speech waveform.
That waveform can lastly be transformed into natural-sounding synthesized speech.
New paper out immediately in @NatMachIntell, the place we present sturdy neural to speech decoding throughout 48 sufferers. https://t.co/rNPAMr4l68 pic.twitter.com/FG7QKCBVzp
— Adeen Flinker 🇮🇱🇺🇦🎗️ (@adeenflinker) April 9, 2024
How the research works
This research includes coaching an AI mannequin that may energy a speech synthesis system, enabling these with speech loss to speak utilizing ideas alone.
Right here’s the way it works in additional element:
1. Gathering mind information
Step one includes gathering the uncooked information wanted to coach the speech-decoding mannequin. The researchers labored with 48 contributors who have been present process neurosurgery for epilepsy.
Through the research, these contributors have been requested to learn tons of of sentences aloud whereas their mind exercise was recorded utilizing ECoG grids.
These grids are positioned straight on the mind’s floor and seize electrical indicators from the mind areas concerned in speech manufacturing.
2. Mapping mind indicators to speech
Utilizing speech information, the researchers developed a complicated AI mannequin that maps the recorded mind indicators to particular speech options, similar to pitch, loudness, and the distinctive frequencies that make up completely different speech sounds.
3. Synthesizing speech from options
The third step focuses on changing the speech options extracted from mind indicators again into audible speech.
The researchers used a particular speech synthesizer that takes the extracted options and generates a spectrogram—a visible illustration of the speech sounds.
4. Evaluating the outcomes
The researchers in contrast the speech generated by their mannequin to the unique speech spoken by the contributors.
They used goal metrics to measure the similarity between the 2 and located that the generated speech carefully matched the unique’s content material and rhythm.
5. Testing on new phrases
To make sure that the mannequin can deal with new phrases it hasn’t seen earlier than, sure phrases have been deliberately disregarded in the course of the mannequin’s coaching section, after which the mannequin’s efficiency on these unseen phrases was examined.
The mannequin’s capacity to precisely decode even new phrases demonstrates its potential to generalize and deal with various speech patterns.
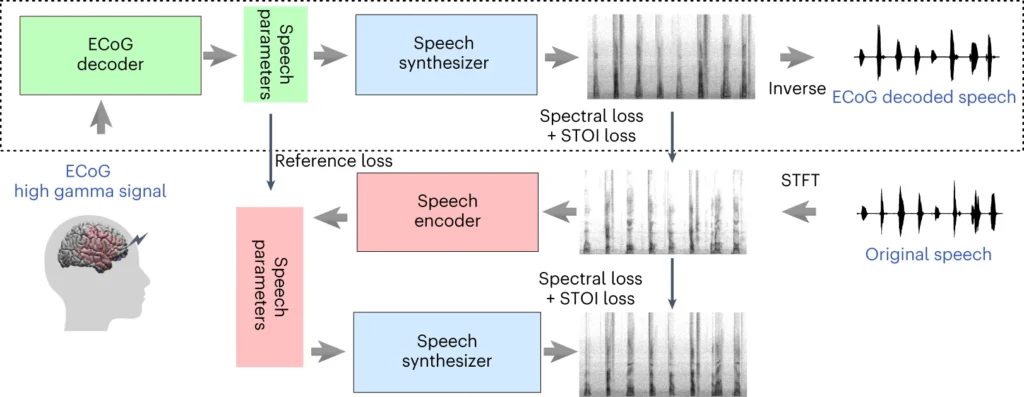
The highest part of the above diagram describes a course of for changing mind indicators to speech. First, a decoder turns these indicators into speech parameters over time. Then, a synthesizer creates sound footage (spectrograms) from these parameters. One other software adjustments these footage again into sound waves.
The underside part discusses a system that helps prepare the mind sign decoder by mimicking speech. It takes a sound image, turns it into speech parameters, after which makes use of these to make a brand new sound image. This a part of the system learns from precise speech sounds to enhance.
After coaching, solely the highest course of is required to show mind indicators into speech.
One key benefit of the NYU method is its capacity to realize high-quality speech decoding with out the necessity for ultra-high-density electrode arrays, that are impractical for long-term implantation.
In essence, it’s a extra light-weight, transportable resolution.
One other notable achievement is the profitable decoding of speech from each the left and proper hemispheres of the mind, which is essential for sufferers with mind injury on one facet of the mind.
Changing ideas to speech utilizing AI
The NYU research builds upon earlier analysis in neural speech decoding and brain-computer interfaces (BCIs).
In 2023, a workforce on the College of California, San Francisco, enabled a paralyzed stroke survivor to generate sentences at a velocity of 78 phrases per minute utilizing a BCI that synthesized each vocalizations and facial expressions from mind indicators.
Different current research have explored using AI to interpret numerous features of human thought from mind exercise. Researchers have demonstrated the power to generate pictures, textual content, and even music from fMRI and EEG information.
For instance, a research from the College of Helsinki used EEG indicators to information a generative adversarial community (GAN) in producing facial pictures that matched contributors’ ideas.
Meta AI additionally developed a way for decoding what somebody was listening to utilizing brainwaves collected non-invasively.
Nonetheless, it stopped in need of predicting speech from thought alone.
Alternatives and challenges
NYU’s methodology makes use of extra broadly accessible and clinically viable electrodes than previous strategies, making it extra accessible.
Whereas these developments are thrilling, main obstacles have to be overcome earlier than mind-reading AI will be broadly utilized.
For one, gathering high-quality mind information requires intensive coaching for machine studying fashions, and particular person variations in mind exercise could make generalization troublesome.
However, the NYU research represents a stride on this course by demonstrating high-accuracy speech decoding utilizing lighterweight ECoG arrays.
Wanting forward, the NYU workforce goals to refine their fashions for real-time speech decoding, bringing us nearer to the last word purpose of enabling pure, fluent conversations for people with speech impairments.
In addition they intend to adapt the system to incorporate absolutely implantable wi-fi units that can be utilized in on a regular basis life.