SUMMARY
- Dubbed AuthQuake; the flaw in Microsoft MFA allowed attackers to bypass safety measures and entry accounts.
- Vulnerability impacted Azure, Workplace 365, and different Microsoft companies with over 400 million customers in danger.
- Exploit leveraged the shortage of charge limiting and prolonged validity of TOTP codes for login periods.
- Attackers may bypass MFA in beneath 70 minutes with a 50% success charge with out person interplay.
- Microsoft patched the flaw completely on October 9, 2024, with stricter rate-limiting mechanisms.
Cybersecurity researchers at Oasis Safety have recognized a vulnerability in Microsoft’s Multi-Issue Authentication (MFA), often called AuthQuake, which permits attackers to bypass safety measures and achieve unauthorized entry to person accounts.
With over 400 million paid Workplace 365 subscriptions, the vulnerability may very well be a extremely profitable alternative for cyber criminals to steal delicate info corresponding to emails, recordsdata, and communications throughout Microsoft’s platforms like Outlook, OneDrive, Groups, Azure, and so forth.
Exploiting Fee Restrict and Time-Based mostly One-Time Password (TOTP)
The exploit takes benefit of two key weaknesses within the MFA setup: Lack of Fee Limiting and Prolonged Timeframe for TOTP Codes. When customers log in, they’re assigned a session ID and requested to confirm their identification utilizing a Time-Based mostly One-Time Password (TOTP) from an authenticator app. The issue is that the system permits as much as 10 failed login makes an attempt per session with out notifying the person or triggering any alerts.
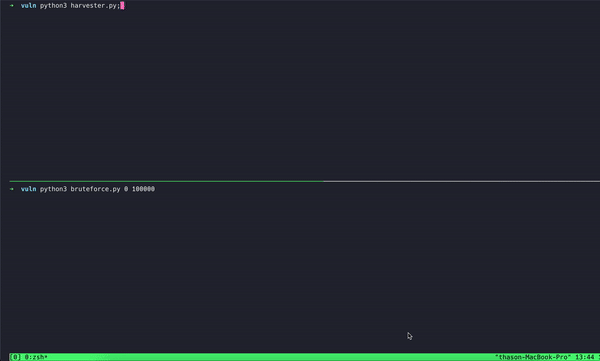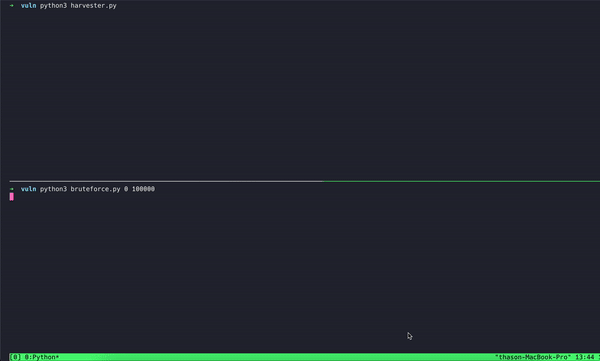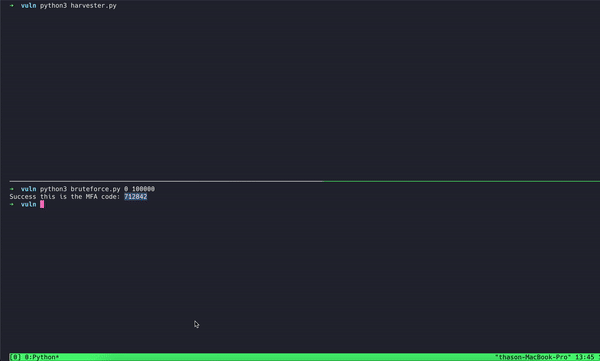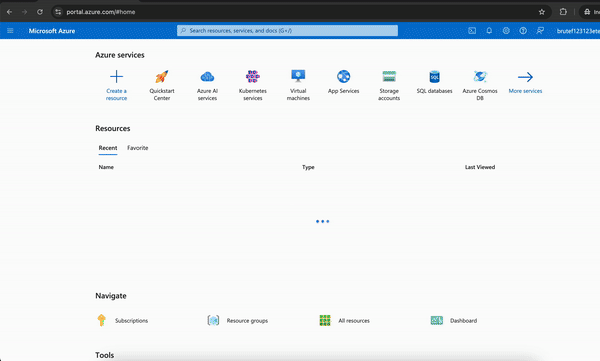
The dearth of charge limiting permits attackers to rapidly create new login periods and trial a number of TOTP codes, that are primarily six-digit numbers. Provided that there are one million attainable mixtures for these codes, an attacker may theoretically exhaust all choices with out encountering any safety measures.
Alternatively, TOTP codes are usually legitimate for under 30 seconds, the testing carried out by Oasis revealed that the system allowed codes to stay legitimate for as much as 3 minutes. This prolonged time-frame considerably will increase the possibilities of success for an attacker trying to guess the proper code.
Outcome?
In keeping with Oasis Safety’s weblog submit shared with Hackread.com forward of its publishing on Wednesday, December 11, researchers concluded that attackers may bypass MFA in beneath 70 minutes with a 50% success charge, all with none person interplay or alerts. Right here’s an indication the researchers created whereas testing the exploit themselves:
Microsoft’s Response
Oasis Safety reported the incident to Microsoft. The tech big was fast to reply and carried out a everlasting repair on October 9, 2024, after a brief repair was deployed on July 4, 2024. The repair concerned introducing stricter charge limits that activate after numerous failed makes an attempt, lasting for about half a day.
Jason Soroko, Senior Fellow at Sectigo, emphasizes the broader implications of this discovery stating, “AuthQuake highlights vital flaws in Microsoft’s MFA implementation. It’s a wake-up name for organizations to undertake patches and rethink their reliance on outdated MFA options. The transfer in direction of passwordless authentication is not only a development however a necessity for future-proofing our safety measures.“
Lesson for Customers and Corporations
Whereas the precise flaw has been patched, organizations ought to inform staff in regards to the significance of cybersecurity and encourage them to report any suspicious login makes an attempt. Furthermore, regardless of the latest points, MFA stays a essential safety measure subsequently, use authenticator apps or discover stronger passwordless strategies for added safety.