Researchers have demonstrated the “first native Spectre v2 exploit” for a brand new speculative execution side-channel flaw that impacts Linux programs working on many trendy Intel processors.
Spectre V2 is a brand new variant of the unique Spectre assault found by a workforce of researchers on the VUSec group from VU Amsterdam.
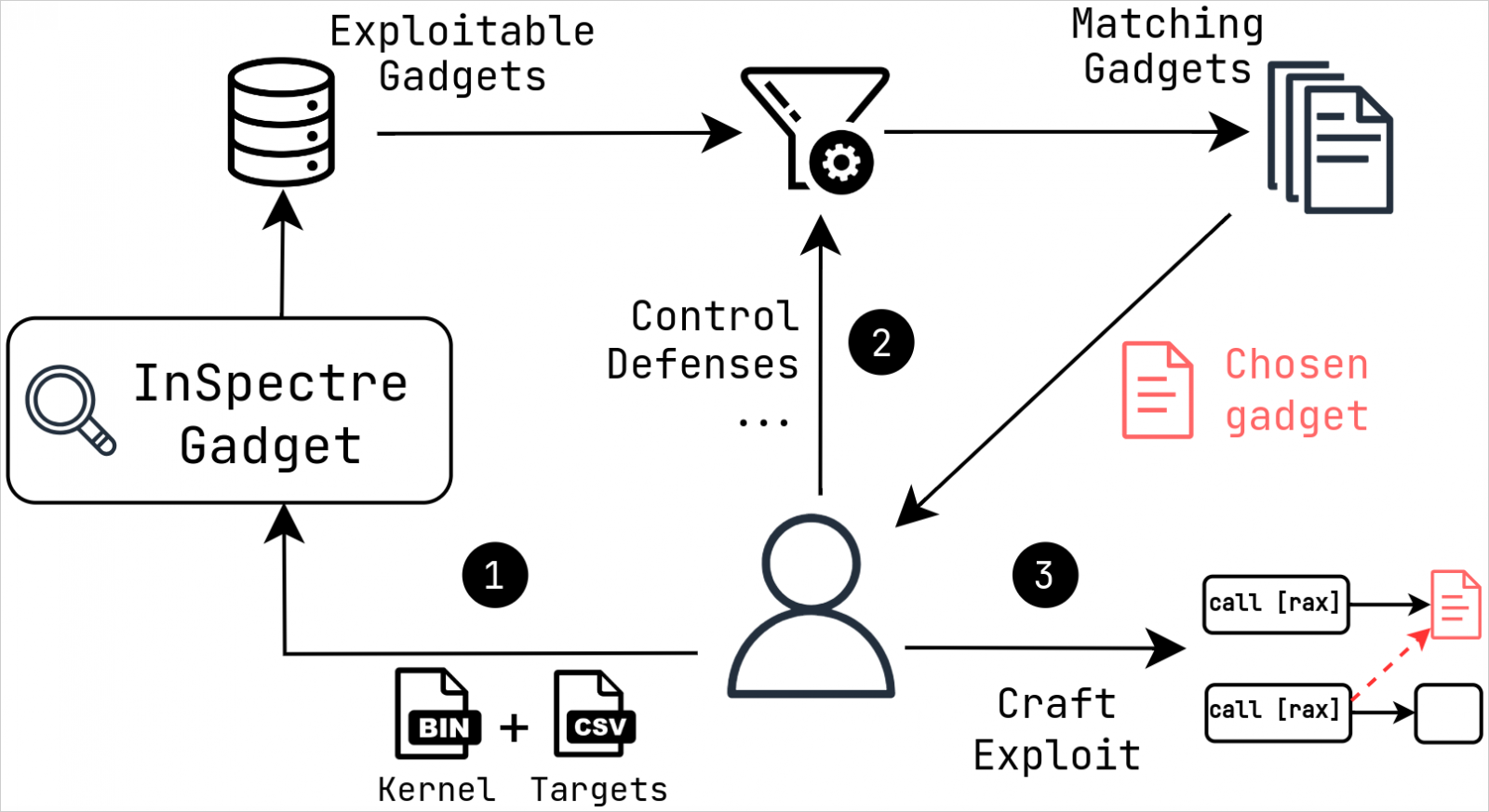
The researchers additionally launched a software that makes use of symbolic execution to determine exploitable code segments inside the Linux kernel to assist with mitigation.
The brand new discovering underscores the challenges in balancing efficiency optimization with safety, which makes addressing basic CPU flaws sophisticated even six years after the discovery of the unique Spectre.
Spectre spooks Linux
Speculative execution is a efficiency optimization method the place trendy processors guess what directions will likely be executed subsequent and begin implementing them earlier than they know they’re wanted. As trendy processors are extraordinarily highly effective, they’ll predict a number of paths a program might take and execute them concurrently.
If one of many guesses is appropriate, there is a rise in software efficiency. If the guesses are improper, the CPU throws away the earlier work and proceeds as ordinary with out altering efficiency.
Nevertheless, whereas this function improves efficiency, it additionally introduces safety dangers by leaving traces of privileged knowledge in CPU caches, which attackers can probably entry.
This knowledge can embody account passwords, encryption keys, delicate private or company data, software program code, and extra.
Two assault strategies are Department Goal Injection (BTI), which includes manipulating the CPU’s department prediction to execute unauthorized code paths, and Department Historical past Injection (BHI), which manipulates department historical past to trigger speculative execution of chosen devices (code paths), resulting in knowledge leakage.
Intel has already assigned CVE-2022-0001 and CVE-2022-0002 to BTI and BHI, respectively, whereas CVE-2024-2201 includes a brand new Spectre v2 exploit that works in opposition to the Linux kernel.
Because the CERT Coordination Middle (CERT/CC) disclosed yesterday, the brand new flaw, tracked as CVE-2024-2201, permits unauthenticated attackers to learn arbitrary reminiscence knowledge by leveraging speculative execution, bypassing current safety mechanisms designed to isolate privilege ranges.
“An unauthenticated attacker can exploit this vulnerability to leak privileged memory from the CPU by speculatively jumping to a chosen gadget,” reads the CERT/CC announcement.
“Current research shows that existing mitigation techniques of disabling privileged eBPF and enabling (Fine)IBT are insufficient in stopping BHI exploitation against the kernel/hypervisor.”
An exploit demonstrating the brand new Spectre V2 flaw could be seen within the video beneath.
Present mitigations are designed round isolating exploitable devices to take away the assault floor. Nevertheless, the VUSec researchers, by their customized ‘InSpectre Gadget‘ evaluation software, demonstrated that exploitable devices within the Linux kernel stay.
- Illumos – Planning so as to add BHI mitigations this week.
- Linux Basis – Subject to be dealt with by the usual {hardware} vulnerability process adopted by the Linux kernel growth workforce.
- Pink Hat – Unprivileged eBPF is disabled by default on RHEL, so the difficulty is not exploitable in normal configurations.
- SUSE Linux – Confirmed impression.
- Triton Information Middle – Really helpful updating to SmartOS 20240418.
- Xen – CERT/CC independently verified impression.
Intel has additionally up to date its mitigation suggestions for Spectre v2 and now proposes disabling unprivileged Prolonged Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF) performance, enabling Enhanced Oblique Department Restricted Hypothesis (eIBRS), and enabling Supervisor Mode Execution Safety (SMEP).
Furthermore, Intel recommends including LFENCE (Load Fence) directions to particular areas within the code to function serialization factors and implementing software program sequences that clear the Department Historical past Buffer (BHB) for transitions between totally different safety domains.
The {hardware} vendor has indicated that future processors will embody mitigations for BHI and probably different speculative execution vulnerabilities.
For a whole checklist of impacted Intel processors to the assorted speculative execution side-channel flaws, verify this web page up to date by the seller.