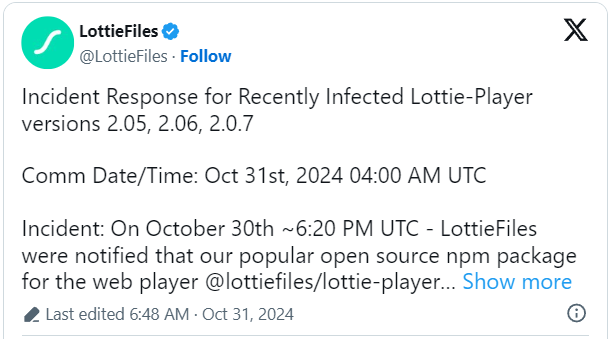
The favored LottieFiles Lotti-Participant undertaking was compromised in a provide chain assault to inject a crypto drainer into web sites that steals guests’ cryptocurrency.
Blockchain menace monitoring platform Rip-off Sniffer stories that no less than one sufferer allegedly misplaced $723,000 price of Bitcoin because of the LottieFiles provide chain compromise.
As found yesterday, following a number of person stories about unusual code injections, Lottie Net Participant (“lottie-player”) 2.0.5, 2.0.6, and a couple of.0.7 had been modified yesterday to incorporate malicious code that injects a crypto pockets drainer into web sites.
Crypto pockets drainers are malicious scripts injected into web sites that show web3 prompts to attach a cryptocurrency pockets. Nevertheless, when a person connects their pockets, the script will robotically try and “drain,” or steal, all property and NFTs and ship them to the menace actors.
LottieFiles rapidly launched model 2.0.8, which is predicated on the clear 2.0.4, advising customers to improve to it as quickly as potential.
“A large number of users using the library via third-party CDNs without a pinned version were automatically served the compromised version as the latest release,” explains LottieFiles CTO Nattu Adnan..
“With the publishing of the safe version, those users would have automatically received the fix.”
These unable to improve to the most recent launch ought to talk the danger to Lottie-player finish customers and warn them about fraudulent cryptocurrency pockets connection requests. Staying on model 2.0.4 can be an possibility.
LottieFiles is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) platform for creating and sharing light-weight vector-based (scalable) animations that may be embedded in apps and web sites.
It is well-liked for permitting high-quality visuals at a minimal efficiency affect on much less highly effective gadgets, cellular, and internet apps.
Provide chain assault masses crypto pockets drainer
Yesterday, builders utilizing the Lottie-Participant script found that they had been affected by a provide chain assault, with web sites utilizing the compromised script abruptly displaying prompts to attach a cryptocurrency pockets.
BleepingComputer examined the malicious model of the Lottie-Participant JavaScript script [VirusTotal] by including it to a easy HTML web page and may affirm that after it was added, the script would load a crypto drainer.
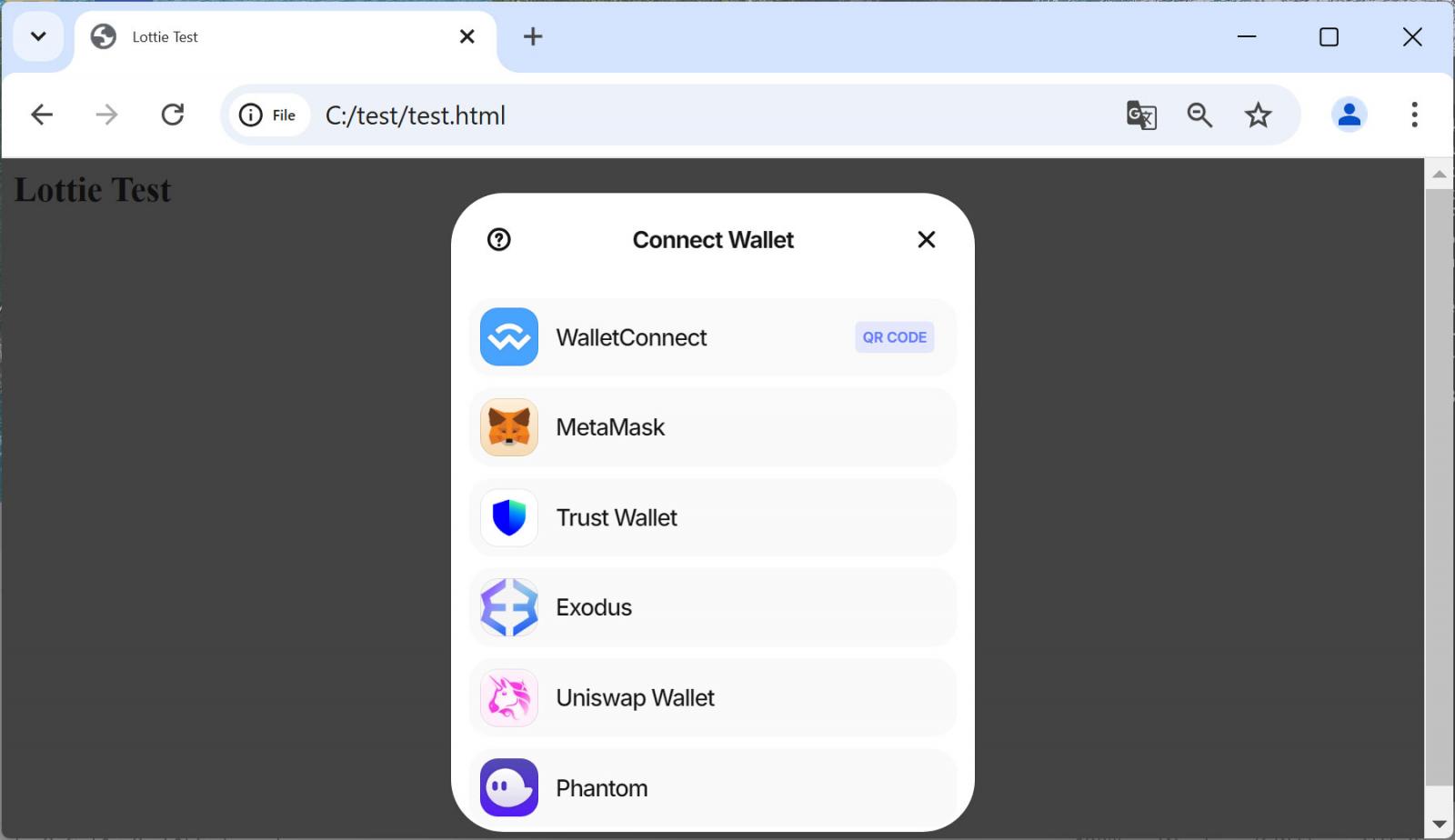
Supply: BleepingComputer
If a customer clicks on one of many buttons to hook up with a pockets, the script will make a WebSocket connection to the positioning castleservices01[.]com [VirusTotal], which has a historical past of being utilized in cryptocurrency phishing assaults.
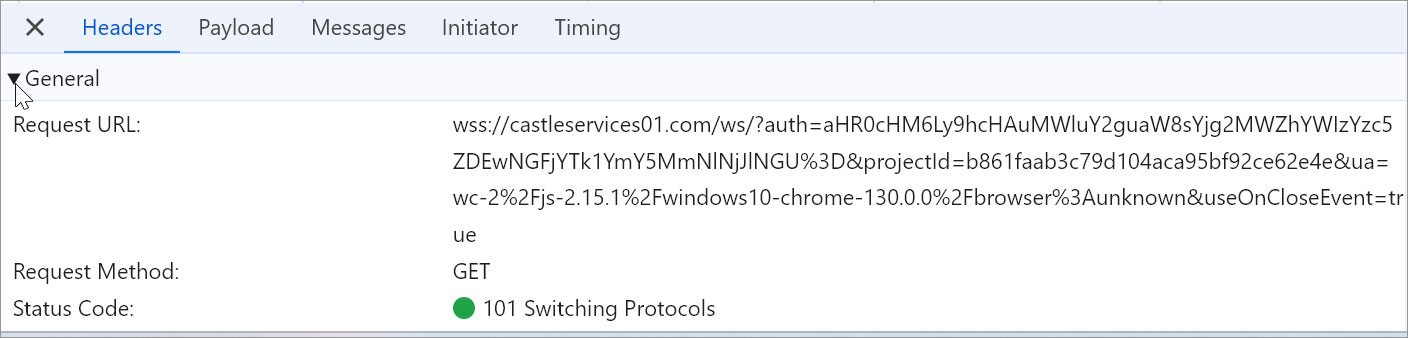
Supply: BleepingComputer
LottieFiles says its JavaScript library was compromised after an authentication token for one among its builders was stolen and used to add the malicious variations of the npm bundle.
“We have confirmed that our other open source libraries, open source code, Github repositories, and our SaaS were not affected,” assures LottieFiles.
The platform continues its inside investigation of the compromise with the assistance of exterior consultants, and extra particulars in regards to the incident could be made out there sooner or later.
The precise variety of victims and quantity of cryptocurrency misplaced to this scheme are unknown presently.
Crypto drainers have turn out to be a large drawback for the cryptocurrency neighborhood, with menace actors hacking well-known X accounts, hacking web sites, and utilizing AI movies and malicious promoting to advertise web sites that make the most of the malicious scripts.
In 2023, Google and Twitter advertisements promoted websites containing a cryptocurrency drainer named ‘MS Drainer’ that stole $59 million from 63,210 victims over 9 months.
