The North Korean hacking group ScarCruft launched a large-scale assault in Might that leveraged an Web Explorer zero-day flaw to contaminate targets with the RokRAT malware and exfiltrate information.
ScarCruft (aka “APT37” or “RedEyes”) is a state-sponsored cyber-espionage menace actor identified for focusing on methods in South Korea and Europe, in addition to North Korean human rights activists and defectors, utilizing phishing, watering gap, and Web Explorer zero-days.
A brand new joint report by South Korea’s Nationwide Cyber Security Middle (NCSC) and AhnLab (ASEC) outlines a latest ScarCruft marketing campaign dubbed “Code on Toast,” which leveraged toast pop-up adverts to carry out zero-click malware infections.
The flaw utilized in zero-day assaults is tracked as CVE-2024-38178 and is a high-severity sort confusion flaw in Web Explorer.
ASEC and NCSC, responding to the marketing campaign, knowledgeable Microsoft instantly, and the tech big launched a safety replace to deal with CVE-2024-39178 in August 2024.
Curiously, the researchers discovered that ScarCruft’s exploit was similar to the one they used previously for CVE-2022-41128, with the one addition being three traces of code designed to bypass Microsoft’s earlier fixes.
From ‘Toast adverts’ to malware
Toast notifications are pop-ups displayed within the nook of software program reminiscent of antivirus or free utility applications to show notifications, alerts, or commercials.
In accordance with AhnLab, APT37 compromised one of many servers of a home promoting company to push specifically crafted ‘Toast adverts’ on an unnamed free software program utilized by numerous South Koreans.
These commercials included a malicious iframe that, when rendered by Web Explorer, brought about a JavaScript file named ‘ad_toast,’ to set off distant code execution by way of the CVE-2024-39178 flaw in Web Explorer’s JScript9.dll file (Chakra engine).
The malware dropped on this assault is a variant of RokRAT, which ScarCruft has been utilizing in assaults for a number of years now.
RokRAT’s main position is to exfiltrate recordsdata matching 20 extensions (together with .doc, .mdb, .xls, .ppt, .txt, .amr) to a Yandex cloud occasion each half-hour.
The malware additionally performs keylogging, displays for clipboard adjustments, and captures screenshots (each 3 minutes).
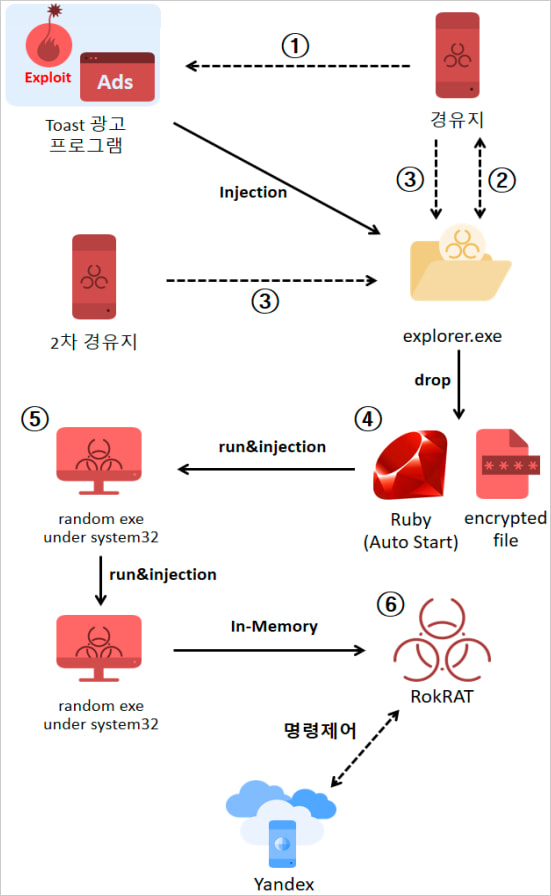
Supply: ASEC
The an infection is carried out by way of a four-step course of the place an equal variety of payloads are injected into the ‘explorer.exe’ course of, evading detection by safety instruments.
If Avast or Symantec antivirus is detected on the host, the malware is injected right into a random executable from the C:Windowssystem32 folder as a substitute.
Persistence is achieved by including a remaining payload (‘rubyw.exe’) to the Home windows startup and registering it for execution within the system’s scheduler each 4 minutes.
Regardless of Microsoft asserting Web Explorer’s retirement in mid-2022, most of the browser’s elements stay in Home windows or are utilized by third-party software program, permitting menace actors to uncover new vulnerabilities to be used in assaults.
This can be occurring with out the customers even realizing they’re on outdated software program that may be simply exploited for zero-click assaults, laying the bottom for mass-scale exploitation by educated menace actors.
What makes this worse is that regardless that Microsoft mounted this specific Web Explorer flaw in August, it doesn’t assure that it will likely be adopted instantly by instruments utilizing older elements. Due to this fact, free software program utilizing outdated Web Explorer elements continues to place customers in danger.
BleepingComputer requested ASEC concerning the variety of impacted customers and the title of the exploited free software program, and we are going to replace you with extra data as soon as obtainable.
